Functions required to prepare X (and y) from a pandas dataframe.
source
apply_sliding_window
apply_sliding_window (data, window_len:int|list, horizon:int|list=0,
x_vars:int|list=None, y_vars:int|list=None)
Applies a sliding window on an array-like input to generate a 3d X (and optionally y)
data
and array-like object with the input data
window_len
int | list
sliding window length. When using a list, use negative numbers and 0.
horizon
int | list
0
horizon
x_vars
int | list
None
indices of the independent variables
y_vars
int | list
None
indices of the dependent variables (target). [] means no y will be created. None means all variables.
source
prepare_sel_vars_and_steps
prepare_sel_vars_and_steps (sel_vars=None, sel_steps=None, idxs=False)
source
prepare_idxs
prepare_idxs (o, shape=None)
= np.arange(20 ).reshape(- 1 ,1 ).repeat(3 , 1 ) * np.array([1 , 10 , 100 ])= pd.DataFrame(data, columns= ['feat_1' , 'feat_2' , 'feat_3' ])
0
0
0
0
1
1
10
100
2
2
20
200
3
3
30
300
4
4
40
400
= 8 = 1 = None = None = apply_sliding_window(data, window_len, horizon= horizon, x_vars= x_vars, y_vars= y_vars)print (np.shares_memory(X, data))print (np.shares_memory(y, data))print (X.shape, y.shape)len (df) - (window_len - 1 + horizon), df.shape[1 ], window_len))len (df) - (window_len - 1 + horizon), df.shape[1 ]))0 ], y[0 ]
True
True
(12, 3, 8) (12, 3)
(array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70],
[ 0, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700]]),
array([ 8, 80, 800]))
= 8 = 1 = None = 0 = apply_sliding_window(df, window_len, horizon= horizon, x_vars= x_vars, y_vars= y_vars)print (np.shares_memory(X, df))print (np.shares_memory(y, df))print (X.shape, y.shape)len (df) - (window_len - 1 + horizon), df.shape[1 ], window_len))len (df) - (window_len - 1 + horizon),))0 ], y[0 ]
True
True
(12, 3, 8) (12,)
(array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70],
[ 0, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700]]),
8)
= 8 = [1 , 2 ]= 0 = [1 , 2 ]= apply_sliding_window(df, window_len, horizon= horizon, x_vars= x_vars, y_vars= y_vars)print (np.shares_memory(X, df))print (np.shares_memory(y, df))print (X.shape, y.shape)len (df) - (window_len - 1 + max (horizon)), 1 , window_len))len (df) - (window_len - 1 + max (horizon)), len (y_vars), len (horizon)))0 ], y[0 ]
True
False
(11, 1, 8) (11, 2, 2)
(array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]]),
array([[ 80, 90],
[800, 900]]))
= [- 4 , - 2 , - 1 , 0 ]= [1 , 2 , 4 ]= 0 = [1 , 2 ]= apply_sliding_window(df, window_len, horizon= horizon, x_vars= x_vars, y_vars= y_vars)print (np.shares_memory(X, df))print (np.shares_memory(y, df))print (X.shape, y.shape)12 , 1 , 4 ))12 , 2 , 3 ))0 ], y[0 ]
False
False
(12, 1, 4) (12, 2, 3)
(array([[0, 2, 3, 4]]),
array([[ 50, 60, 80],
[500, 600, 800]]))
source
df2Xy
df2Xy (df, sample_col=None, feat_col=None, data_cols=None,
target_col=None, steps_in_rows=False, to3d=True, splits=None,
sort_by=None, ascending=True, y_func=None, return_names=False)
This function allows you to transform a pandas dataframe into X and y numpy arrays that can be used to create a TSDataset. sample_col: column that uniquely identifies each sample. feat_col: used for multivariate datasets. It indicates which is the column that indicates the feature by row. data_col: indicates ths column/s where the data is located. If None, it means all columns (except the sample_col, feat_col, and target_col) target_col: indicates the column/s where the target is. steps_in_rows: flag to indicate if each step is in a different row or in a different column (default). to3d: turns X to 3d (including univariate time series) sort_by: this is used to pass any colum/s that are needed to sort the steps in the sequence. If you pass a sample_col and/ or feat_col these will be automatically used before the sort_by column/s, and you don’t need to add them to the sort_by column/s list. y_func: function used to calculate y for each sample (and target_col) return_names: flag to return the names of the columns from where X was generated
source
split_Xy
split_Xy (X, y=None, splits=None)
= pd.DataFrame()'sample_id' ] = np.array([1 ,1 ,1 ,2 ,2 ,2 ,3 ,3 ,3 ])'var1' ] = df['sample_id' ] * 10 + df.index.values'var2' ] = df['sample_id' ] * 100 + df.index.values
0
1
10
100
1
1
11
101
2
1
12
102
3
2
23
203
4
2
24
204
5
2
25
205
6
3
36
306
7
3
37
307
8
3
38
308
= df2Xy(df, sample_col= 'sample_id' , steps_in_rows= True )0 ], np.array([[10 , 11 , 12 ], [100 , 101 , 102 ]]))
= 1_000 = 10_000 = np.arange(n_samples).repeat(n_rows// n_samples).reshape(- 1 ,1 )= np.tile(np.arange(n_rows // n_samples), n_samples).reshape(- 1 ,1 )= np.random.randn(n_rows, 6 )= np.random.randint(0 , 3 , (n_rows, 1 ))= np.array([0 ,1 ,2 ])[ind_cat]= np.random.randint(0 , 3 , (n_rows, 1 ))= np.array([100 ,200 ,300 ])[ind_cat2]= np.concatenate([sample_ids, feat_ids, cont, target, target], - 1 )= ['sample_id' , 'feat_id' ] + (np.arange(6 ) + 1 ).astype(str ).tolist() + ['target' ] + ['target2' ]= pd.DataFrame(data, columns= columns)= random_choice(np.arange(len (df)), len (df), False )= {'sample_id' :np.int32, 'feat_id' :np.int32, '1' :np.float32, '2' :np.float32, '3' :np.float32, '4' :np.float32, '5' :np.float32, '6' :np.float32}= df.astype(dtype= new_dtypes)= df.loc[idx].reset_index(drop= True )
0
625
2
-1.390549
0.770179
-0.848480
0.853631
-0.309984
0.874338
2.0
2.0
1
526
4
1.152397
2.064397
-0.392603
-0.275797
-0.047526
-2.248814
2.0
2.0
2
397
6
-1.052930
0.631396
-0.758800
-0.606483
-2.776054
-0.457755
1.0
1.0
3
528
8
-0.178637
-1.253319
-1.154014
0.913876
1.051010
-0.635762
1.0
1.0
4
249
2
0.612595
0.888297
0.065024
1.621935
-0.180479
0.309977
1.0
1.0
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
9995
272
1
-0.432325
1.645262
1.502872
-1.144859
0.919653
0.414304
0.0
0.0
9996
920
5
-0.724702
-1.471832
1.209086
1.206532
0.555676
0.352726
2.0
2.0
9997
662
6
1.122043
-0.379357
-0.344517
-1.545091
0.187894
1.062510
2.0
2.0
9998
71
7
-0.053582
-0.854992
-1.118632
-1.967820
-0.344804
0.128105
0.0
0.0
9999
407
4
-1.565716
-0.947183
-0.401944
-1.309024
-0.237755
-0.743251
2.0
2.0
10000 rows × 10 columns
from scipy.stats import mode
def y_func(o): return mode(o, axis= 1 , keepdims= True ).mode= df2xy(df, sample_col= 'sample_id' , feat_col= 'feat_id' , target_col= ['target' , 'target2' ], sort_by= ['sample_id' , 'feat_id' ], y_func= y_func)1000 , 10 , 6 ))1000 , 2 ))= np.random.randint(0 , np.max (df.sample_id))= df.sort_values(by= ['sample_id' , 'feat_id' ], kind= 'stable' ).reset_index(drop= True )== rand_idx][['1' , '2' , '3' , '4' , '5' , '6' ]].values)== rand_idx][['target' , 'target2' ]].values).mode), y[rand_idx])
# Univariate from io import StringIO
= StringIO("""sample_id;value_0;value_1;target rob;2;3;0 alice;6;7;1 eve;11;12;2 """ )= pd.read_csv(TESTDATA, sep= ";" )= df2Xy(df, sample_col= 'sample_id' , target_col= 'target' , data_cols= ['value_0' , 'value_1' ], sort_by= 'sample_id' )3 , 1 , 2 ))3 ,))
0
rob
2
3
0
1
alice
6
7
1
2
eve
11
12
2
(array([[[ 6, 7]],
[[11, 12]],
[[ 2, 3]]]),
array([1, 2, 0]))
# Univariate = StringIO("""sample_id;timestep;values;target rob;1;2;0 alice;1;6;1 eve;1;11;2 rob;2;3;0 alice;2;7;1 eve;2;12;2 """ )= pd.read_csv(TESTDATA, sep= ";" )def y_func(o): return mode(o, axis= 1 ).mode= df2xy(df, sample_col= 'sample_id' , target_col= 'target' , data_cols= ['values' ], sort_by= 'timestep' , to3d= True , y_func= y_func)3 , 1 , 2 ))3 , ))print (X, y)
0
rob
1
2
0
1
alice
1
6
1
2
eve
1
11
2
3
rob
2
3
0
4
alice
2
7
1
5
eve
2
12
2
[[[ 6 7]]
[[11 12]]
[[ 2 3]]] [1 2 0]
# Multivariate = StringIO("""sample_id;trait;value_0;value_1;target rob;green;2;3;0 rob;yellow;3;4;0 rob;blue;4;5;0 rob;red;5;6;0 alice;green;6;7;1 alice;yellow;7;8;1 alice;blue;8;9;1 alice;red;9;10;1 eve;yellow;11;12;2 eve;green;10;11;2 eve;blue;12;12;2 eve;red;13;14;2 """ )= pd.read_csv(TESTDATA, sep= ";" )= random_choice(len (df), len (df), False )= df.iloc[idx]def y_func(o): return mode(o, axis= 1 ).mode= df2xy(df, sample_col= 'sample_id' , feat_col= 'trait' , target_col= 'target' , data_cols= ['value_0' , 'value_1' ], y_func= y_func)print (X, y)3 , 4 , 2 ))3 ,))
9
eve
green
10
11
2
10
eve
blue
12
12
2
3
rob
red
5
6
0
0
rob
green
2
3
0
6
alice
blue
8
9
1
2
rob
blue
4
5
0
1
rob
yellow
3
4
0
4
alice
green
6
7
1
7
alice
red
9
10
1
8
eve
yellow
11
12
2
11
eve
red
13
14
2
5
alice
yellow
7
8
1
[[[ 8 9]
[ 6 7]
[ 9 10]
[ 7 8]]
[[12 12]
[10 11]
[13 14]
[11 12]]
[[ 4 5]
[ 2 3]
[ 5 6]
[ 3 4]]] [1 2 0]
# Multivariate, multi-label = StringIO("""sample_id;trait;value_0;value_1;target1;target2 rob;green;2;3;0;0 rob;yellow;3;4;0;0 rob;blue;4;5;0;0 rob;red;5;6;0;0 alice;green;6;7;1;0 alice;yellow;7;8;1;0 alice;blue;8;9;1;0 alice;red;9;10;1;0 eve;yellow;11;12;2;1 eve;green;10;11;2;1 eve;blue;12;12;2;1 eve;red;13;14;2;1 """ )= pd.read_csv(TESTDATA, sep= ";" )def y_func(o): return mode(o, axis= 1 , keepdims= True ).mode= df2xy(df, sample_col= 'sample_id' , feat_col= 'trait' , target_col= ['target1' , 'target2' ], data_cols= ['value_0' , 'value_1' ], y_func= y_func)3 , 4 , 2 ))3 , 2 ))print (X, y)
0
rob
green
2
3
0
0
1
rob
yellow
3
4
0
0
2
rob
blue
4
5
0
0
3
rob
red
5
6
0
0
4
alice
green
6
7
1
0
5
alice
yellow
7
8
1
0
6
alice
blue
8
9
1
0
7
alice
red
9
10
1
0
8
eve
yellow
11
12
2
1
9
eve
green
10
11
2
1
10
eve
blue
12
12
2
1
11
eve
red
13
14
2
1
[[[ 8 9]
[ 6 7]
[ 9 10]
[ 7 8]]
[[12 12]
[10 11]
[13 14]
[11 12]]
[[ 4 5]
[ 2 3]
[ 5 6]
[ 3 4]]] [[1 0]
[2 1]
[0 0]]
# Multivariate, unlabeled = StringIO("""sample_id;trait;value_0;value_1;target rob;green;2;3;0 rob;yellow;3;4;0 rob;blue;4;5;0 rob;red;5;6;0 alice;green;6;7;1 alice;yellow;7;8;1 alice;blue;8;9;1 alice;red;9;10;1 eve;yellow;11;12;2 eve;green;10;11;2 eve;blue;12;12;2 eve;red;13;14;2 """ )= pd.read_csv(TESTDATA, sep= ";" )= random_choice(len (df), len (df), False )= df.iloc[idx]def y_func(o): return mode(o, axis= 1 , keepdims= True ).mode= df2xy(df, sample_col= 'sample_id' , feat_col= 'trait' , data_cols= ['value_0' , 'value_1' ], y_func= y_func)print (X, y)3 , 4 , 2 ))None )
11
eve
red
13
14
2
3
rob
red
5
6
0
9
eve
green
10
11
2
10
eve
blue
12
12
2
6
alice
blue
8
9
1
1
rob
yellow
3
4
0
4
alice
green
6
7
1
2
rob
blue
4
5
0
0
rob
green
2
3
0
8
eve
yellow
11
12
2
7
alice
red
9
10
1
5
alice
yellow
7
8
1
[[[ 8 9]
[ 6 7]
[ 9 10]
[ 7 8]]
[[12 12]
[10 11]
[13 14]
[11 12]]
[[ 4 5]
[ 2 3]
[ 5 6]
[ 3 4]]] None
= StringIO("""sample_id;trait;timestep;values;target rob;green;1;2;0 rob;yellow;1;3;0 rob;blue;1;4;0 rob;red;1;5;0 alice;green;1;6;1 alice;yellow;1;7;1 alice;blue;1;8;1 alice;red;1;9;1 eve;yellow;1;11;2 eve;green;1;10;2 eve;blue;1;12;2 eve;red;1;13;2 rob;green;2;3;0 rob;yellow;2;4;0 rob;blue;2;5;0 rob;red;2;6;0 alice;green;2;7;1 alice;yellow;2;8;1 alice;blue;2;9;1 alice;red;2;10;1 eve;yellow;2;12;2 eve;green;2;11;2 eve;blue;2;13;2 eve;red;2;14;2 """ )= pd.read_csv(TESTDATA, sep= ";" )def y_func(o): return mode(o, axis= 1 ).mode= df2xy(df, sample_col= 'sample_id' , feat_col= 'trait' , sort_by= 'timestep' , target_col= 'target' , data_cols= ['values' ], y_func= y_func)print (X, y)3 , 4 , 2 ))3 , ))
0
rob
green
1
2
0
1
rob
yellow
1
3
0
2
rob
blue
1
4
0
3
rob
red
1
5
0
4
alice
green
1
6
1
5
alice
yellow
1
7
1
6
alice
blue
1
8
1
7
alice
red
1
9
1
8
eve
yellow
1
11
2
9
eve
green
1
10
2
10
eve
blue
1
12
2
11
eve
red
1
13
2
12
rob
green
2
3
0
13
rob
yellow
2
4
0
14
rob
blue
2
5
0
15
rob
red
2
6
0
16
alice
green
2
7
1
17
alice
yellow
2
8
1
18
alice
blue
2
9
1
19
alice
red
2
10
1
20
eve
yellow
2
12
2
21
eve
green
2
11
2
22
eve
blue
2
13
2
23
eve
red
2
14
2
[[[ 8 9]
[ 6 7]
[ 9 10]
[ 7 8]]
[[12 13]
[10 11]
[13 14]
[11 12]]
[[ 4 5]
[ 2 3]
[ 5 6]
[ 3 4]]] [1 2 0]
source
df2np3d
df2np3d (df, groupby, data_cols=None)
Transforms a df (with the same number of rows per group in groupby) to a 3d ndarray
= np.array([1 ,2 ]).repeat(4 ).reshape(- 1 ,1 )= np.random.rand(8 , 3 )= np.concatenate([user, val], axis=- 1 )= pd.DataFrame(data, columns= ['user' , 'x1' , 'x2' , 'x3' ])'user' ], ['x1' , 'x2' , 'x3' ]).shape, (2 , 3 , 4 ))
source
add_missing_value_cols
add_missing_value_cols (df, cols=None, dtype=<class 'float'>,
fill_value=None)
= np.random.randn(10 , 2 )= data > .8 = np.nan= pd.DataFrame(data, columns= ['A' , 'B' ])= add_missing_value_cols(df, cols= None , dtype= float )'A' ].isnull().sum (), df['missing_A' ].sum ())'B' ].isnull().sum (), df['missing_B' ].sum ())
0
0.476712
-0.880797
0.0
0.0
1
NaN
-1.517210
1.0
0.0
2
-1.348997
-0.878441
0.0
0.0
3
NaN
0.290756
1.0
0.0
4
0.569218
-1.415777
0.0
0.0
5
0.591641
-2.133860
0.0
0.0
6
NaN
NaN
1.0
1.0
7
NaN
-0.119397
1.0
0.0
8
-0.727988
0.057254
0.0
0.0
9
-0.631352
-0.219028
0.0
0.0
source
add_missing_timestamps
add_missing_timestamps (df, datetime_col=None, use_index=False,
unique_id_cols=None, groupby=None,
fill_value=nan, range_by_group=True,
start_date=None, end_date=None, freq=None)
df
pandas DataFrame
datetime_col
NoneType
None
column that contains the datetime data (without duplicates within groups)
use_index
bool
False
indicates if the index contains the datetime data
unique_id_cols
NoneType
None
column used to identify unique_ids
groupby
NoneType
None
same as unique_id_cols. Will be deprecated. Kept for compatiblity.
fill_value
float
nan
values that will be insert where missing dates exist. Default:np.nan
range_by_group
bool
True
if True, dates will be filled between min and max dates for each group. Otherwise, between the min and max dates in the df.
start_date
NoneType
None
start date to fill in missing dates (same for all unique_ids)
end_date
NoneType
None
end date to fill in missing dates (same for all unique_ids)
freq
NoneType
None
frequency used to fill in the missing datetime
# Filling dates between min and max dates = pd.date_range('2021-05-01' , '2021-05-07' ).values= np.zeros((len (dates), 3 ))0 ] = dates1 ] = np.random.rand(len (dates))2 ] = np.random.rand(len (dates))= ['date' , 'feature1' , 'feature2' ]= pd.DataFrame(data, columns= cols).astype({'date' : 'datetime64[ns]' , 'feature1' : float , 'feature2' : float })= date_df.drop([1 ,3 ]).reset_index(drop= True )
0
2021-05-01
0.537248
0.670897
1
2021-05-03
0.299912
0.421039
2
2021-05-05
0.648372
0.204641
3
2021-05-06
0.017475
0.022183
4
2021-05-07
0.965919
0.470055
# No groups = date_df.copy()1 ,3 ], ['feature1' , 'feature2' ]] = np.nan= add_missing_timestamps(date_df_with_missing_dates.copy(), 'date' , = None , = np.nan, = False )
0
2021-05-01
0.537248
0.670897
1
2021-05-02
NaN
NaN
2
2021-05-03
0.299912
0.421039
3
2021-05-04
NaN
NaN
4
2021-05-05
0.648372
0.204641
5
2021-05-06
0.017475
0.022183
6
2021-05-07
0.965919
0.470055
# Filling dates between min and max dates for each value in groupby column = pd.date_range('2021-05-01' , '2021-05-07' ).values= np.concatenate((dates, dates))= np.zeros((len (dates), 4 ))0 ] = dates1 ] = np.array([0 ]* (len (dates)// 2 )+ [1 ]* (len (dates)// 2 ))2 ] = np.random.rand(len (dates))3 ] = np.random.rand(len (dates))= ['date' , 'id' , 'feature1' , 'feature2' ]= pd.DataFrame(data, columns= cols).astype({'date' : 'datetime64[ns]' , 'id' : int , 'feature1' : float , 'feature2' : float })= date_df.drop([0 ,1 ,3 ,8 ,11 ,13 ]).reset_index(drop= True )
0
2021-05-03
0
0.059398
0.255853
1
2021-05-05
0
0.235536
0.455261
2
2021-05-06
0
0.724423
0.280910
3
2021-05-07
0
0.303682
0.853959
4
2021-05-01
1
0.022424
0.408510
5
2021-05-03
1
0.508190
0.603880
6
2021-05-04
1
0.330924
0.108156
7
2021-05-06
1
0.601481
0.020182
# groupby='id', range_by_group=True = date_df.drop([0 ,1 ,13 ]).reset_index(drop= True ) 1 ,6 ,9 ], ['feature1' , 'feature2' ]] = np.nan= add_missing_timestamps(date_df_with_missing_dates.copy(), 'date' , = 'id' , = np.nan, = True )
0
2021-05-03
0
0.059398
0.255853
1
2021-05-04
0
NaN
NaN
2
2021-05-05
0
0.235536
0.455261
3
2021-05-06
0
0.724423
0.280910
4
2021-05-07
0
0.303682
0.853959
5
2021-05-01
1
0.022424
0.408510
6
2021-05-02
1
NaN
NaN
7
2021-05-03
1
0.508190
0.603880
8
2021-05-04
1
0.330924
0.108156
9
2021-05-05
1
NaN
NaN
10
2021-05-06
1
0.601481
0.020182
# groupby='id', range_by_group=False = date_df.copy() 0 ,1 ,3 ,8 ,11 ,13 ], ['feature1' , 'feature2' ]] = np.nan= add_missing_timestamps(date_df_with_missing_dates.copy(), 'date' , = 'id' , = np.nan, = False )
0
2021-05-01
0
NaN
NaN
1
2021-05-02
0
NaN
NaN
2
2021-05-03
0
0.059398
0.255853
3
2021-05-04
0
NaN
NaN
4
2021-05-05
0
0.235536
0.455261
5
2021-05-06
0
0.724423
0.280910
6
2021-05-07
0
0.303682
0.853959
7
2021-05-01
1
0.022424
0.408510
8
2021-05-02
1
NaN
NaN
9
2021-05-03
1
0.508190
0.603880
10
2021-05-04
1
0.330924
0.108156
11
2021-05-05
1
NaN
NaN
12
2021-05-06
1
0.601481
0.020182
13
2021-05-07
1
NaN
NaN
# Filling dates between min and max timestamps = pd.date_range('2021-05-01 000:00' , '2021-05-01 20:00' , freq= '4H' ).values= np.zeros((len (dates), 3 ))0 ] = dates1 ] = np.random.rand(len (dates))2 ] = np.random.rand(len (dates))= ['date' , 'feature1' , 'feature2' ]= pd.DataFrame(data, columns= cols).astype({'date' : 'datetime64[ns]' , 'feature1' : float , 'feature2' : float })= date_df.drop([1 ,3 ]).reset_index(drop= True )
0
2021-05-01 00:00:00
0.774846
0.624488
1
2021-05-01 08:00:00
0.683837
0.441230
2
2021-05-01 16:00:00
0.142269
0.279095
3
2021-05-01 20:00:00
0.953686
0.205123
# No groups = date_df.copy()1 ,3 ], ['feature1' , 'feature2' ]] = np.nan= add_missing_timestamps(date_df_with_missing_dates.copy(), 'date' , groupby= None , fill_value= np.nan, range_by_group= False , freq= '4H' )
0
2021-05-01 00:00:00
0.774846
0.624488
1
2021-05-01 04:00:00
NaN
NaN
2
2021-05-01 08:00:00
0.683837
0.441230
3
2021-05-01 12:00:00
NaN
NaN
4
2021-05-01 16:00:00
0.142269
0.279095
5
2021-05-01 20:00:00
0.953686
0.205123
# Filling missing values between min and max timestamps for each value in groupby column = pd.date_range('2021-05-01 000:00' , '2021-05-01 20:00' , freq= '4H' ).values= np.concatenate((dates, dates))= np.zeros((len (dates), 4 ))0 ] = dates1 ] = np.array([0 ]* (len (dates)// 2 )+ [1 ]* (len (dates)// 2 ))2 ] = np.random.rand(len (dates))3 ] = np.random.rand(len (dates))= ['date' , 'id' , 'feature1' , 'feature2' ]= pd.DataFrame(data, columns= cols).astype({'date' : 'datetime64[ns]' , 'id' : int , 'feature1' : float , 'feature2' : float })= date_df.drop([0 ,1 ,3 ,8 ,9 ,11 ]).reset_index(drop= True )
0
2021-05-01 08:00:00
0
0.438784
0.084472
1
2021-05-01 16:00:00
0
0.059613
0.445215
2
2021-05-01 20:00:00
0
0.511807
0.001034
3
2021-05-01 00:00:00
1
0.970115
0.280121
4
2021-05-01 04:00:00
1
0.775051
0.436359
5
2021-05-01 16:00:00
1
0.469987
0.457442
# groupby='id', range_by_group=True = date_df.drop([0 ,1 ,11 ]).reset_index(drop= True ) 1 ,6 ,7 ], ['feature1' , 'feature2' ]] = np.nan= add_missing_timestamps(date_df_with_missing_dates.copy(),'date' , = 'id' , = np.nan, = True , = '4H' )
0
2021-05-01 08:00:00
0
0.438784
0.084472
1
2021-05-01 12:00:00
0
NaN
NaN
2
2021-05-01 16:00:00
0
0.059613
0.445215
3
2021-05-01 20:00:00
0
0.511807
0.001034
4
2021-05-01 00:00:00
1
0.970115
0.280121
5
2021-05-01 04:00:00
1
0.775051
0.436359
6
2021-05-01 08:00:00
1
NaN
NaN
7
2021-05-01 12:00:00
1
NaN
NaN
8
2021-05-01 16:00:00
1
0.469987
0.457442
# groupby='id', range_by_group=False = date_df.copy() 0 ,1 ,3 ,8 ,9 ,11 ], ['feature1' , 'feature2' ]] = np.nan= add_missing_timestamps(date_df_with_missing_dates.copy(), 'date' , = 'id' , = np.nan, = False , = '4H' )
0
2021-05-01 00:00:00
0
NaN
NaN
1
2021-05-01 04:00:00
0
NaN
NaN
2
2021-05-01 08:00:00
0
0.438784
0.084472
3
2021-05-01 12:00:00
0
NaN
NaN
4
2021-05-01 16:00:00
0
0.059613
0.445215
5
2021-05-01 20:00:00
0
0.511807
0.001034
6
2021-05-01 00:00:00
1
0.970115
0.280121
7
2021-05-01 04:00:00
1
0.775051
0.436359
8
2021-05-01 08:00:00
1
NaN
NaN
9
2021-05-01 12:00:00
1
NaN
NaN
10
2021-05-01 16:00:00
1
0.469987
0.457442
11
2021-05-01 20:00:00
1
NaN
NaN
# No groups, with duplicate dates ==> FAILS = pd.date_range('2021-05-01 000:00' , '2021-05-01 20:00' , freq= '4H' ).values= np.zeros((len (dates), 3 ))0 ] = dates1 ] = np.random.rand(len (dates))2 ] = np.random.rand(len (dates))= ['date' , 'feature1' , 'feature2' ]= pd.DataFrame(data, columns= cols).astype({'date' : 'datetime64[ns]' , 'feature1' : float , 'feature2' : float })= date_df.drop([1 ,3 ]).reset_index(drop= True )3 , 'date' ] = date_df_with_missing_dates.loc[2 , 'date' ]= [date_df_with_missing_dates, 'date' ], kwargs= dict (groupby= None , fill_value= np.nan, range_by_group= False , freq= '4H' ), )
0
2021-05-01 00:00:00
0.755092
0.002068
1
2021-05-01 08:00:00
0.570693
0.087019
2
2021-05-01 16:00:00
0.228869
0.856618
3
2021-05-01 16:00:00
0.349506
0.428253
# groupby='id', range_by_group=True, with duplicate dates ==> FAILS = pd.date_range('2021-05-01 000:00' , '2021-05-01 20:00' , freq= '4H' ).values= np.concatenate((dates, dates))= np.zeros((len (dates), 4 ))0 ] = dates1 ] = np.array([0 ]* (len (dates)// 2 )+ [1 ]* (len (dates)// 2 ))2 ] = np.random.rand(len (dates))3 ] = np.random.rand(len (dates))= ['date' , 'id' , 'feature1' , 'feature2' ]= pd.DataFrame(data, columns= cols).astype({'date' : 'datetime64[ns]' , 'id' : int , 'feature1' : float , 'feature2' : float })= date_df.drop([0 ,1 ,8 ,9 ,11 ]).reset_index(drop= True )3 , 'date' ] = date_df_with_missing_dates.loc[2 , 'date' ]= [date_df_with_missing_dates, 'date' ], kwargs= dict (groupby= 'id' , fill_value= np.nan, range_by_group= True , freq= '4H' ), = 'cannot handle a non-unique multi-index!' )
0
2021-05-01 08:00:00
0
0.040345
0.312874
1
2021-05-01 12:00:00
0
0.713424
0.597211
2
2021-05-01 16:00:00
0
0.468382
0.652314
3
2021-05-01 16:00:00
0
0.396691
0.605664
4
2021-05-01 00:00:00
1
0.804646
0.964115
5
2021-05-01 04:00:00
1
0.089925
0.072410
6
2021-05-01 16:00:00
1
0.830786
0.560658
# groupby='id', range_by_group=FALSE, with duplicate dates ==> FAILS = pd.date_range('2021-05-01 000:00' , '2021-05-01 20:00' , freq= '4H' ).values= np.concatenate((dates, dates))= np.zeros((len (dates), 4 ))0 ] = dates1 ] = np.array([0 ]* (len (dates)// 2 )+ [1 ]* (len (dates)// 2 ))2 ] = np.random.rand(len (dates))3 ] = np.random.rand(len (dates))= ['date' , 'id' , 'feature1' , 'feature2' ]= pd.DataFrame(data, columns= cols).astype({'date' : 'datetime64[ns]' , 'id' : int , 'feature1' : float , 'feature2' : float })= date_df.drop([0 ,1 ,8 ,9 ,11 ]).reset_index(drop= True )3 , 'date' ] = date_df_with_missing_dates.loc[2 , 'date' ]= [date_df_with_missing_dates, 'date' ], kwargs= dict (groupby= 'id' , fill_value= np.nan, range_by_group= False , freq= '4H' ), = 'cannot handle a non-unique multi-index!' )
0
2021-05-01 08:00:00
0
0.448508
0.953596
1
2021-05-01 12:00:00
0
0.868802
0.526845
2
2021-05-01 16:00:00
0
0.223070
0.304842
3
2021-05-01 16:00:00
0
0.645661
0.270956
4
2021-05-01 00:00:00
1
0.017250
0.787757
5
2021-05-01 04:00:00
1
0.783341
0.608269
6
2021-05-01 16:00:00
1
0.426247
0.926149
source
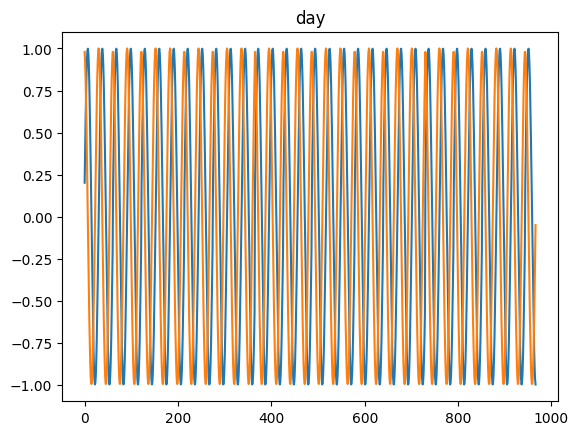
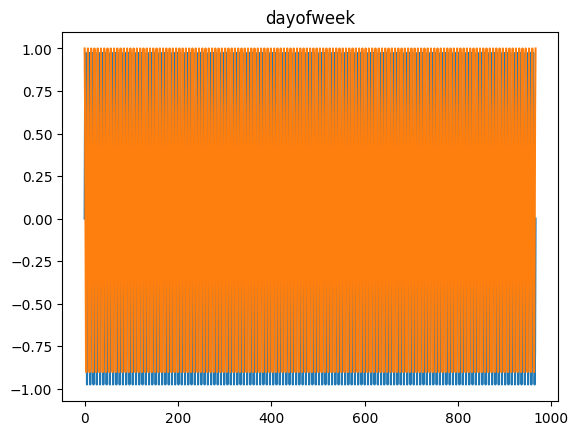
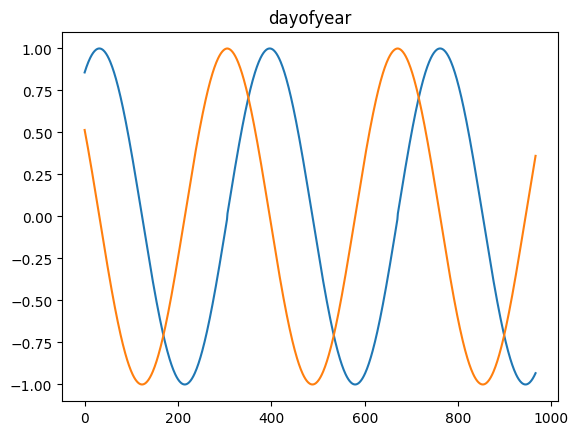
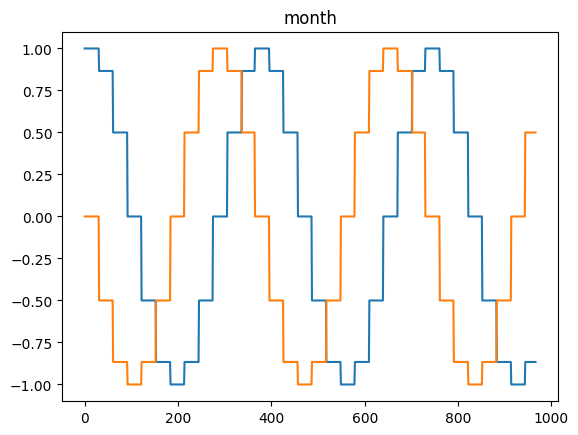
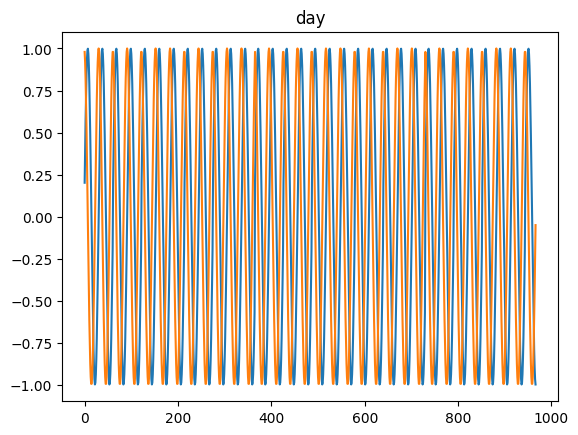
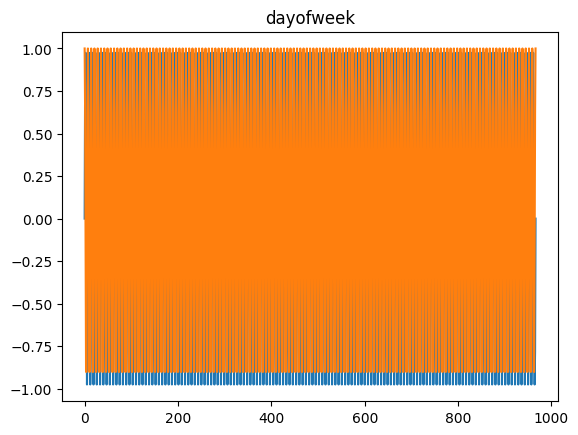
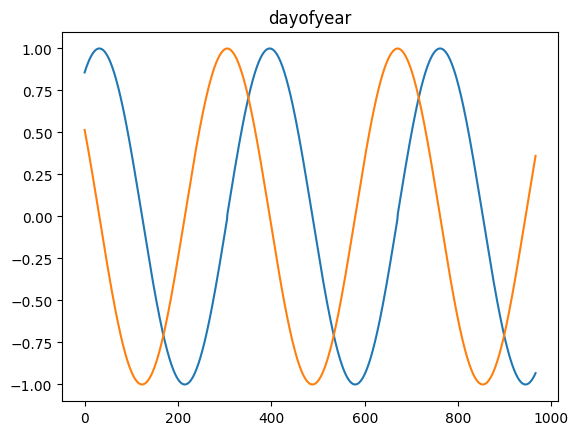
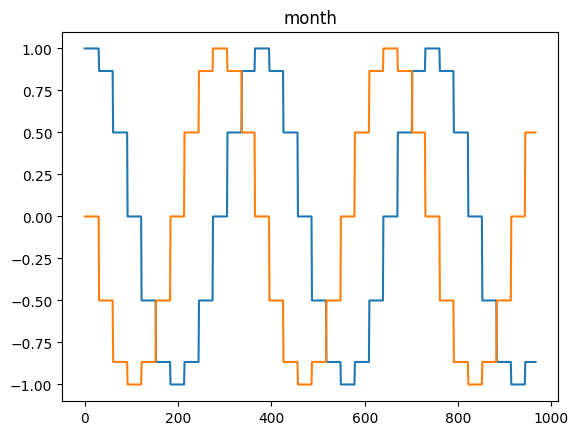
time_encoding
time_encoding (series, freq, max_val=None)
*Transforms a pandas series of dtype datetime64 (of any freq) or DatetimeIndex into 2 float arrays
Available options: microsecond, millisecond, second, minute, hour, day = day_of_month = dayofmonth, day_of_week = weekday = dayofweek, day_of_year = dayofyear, week = week_of_year = weekofyear, month and year*
for freq in ['microsecond' , 'second' , 'minute' , 'hour' , 'day' , 'dayofweek' , 'dayofyear' , 'month' ]:= pd.DataFrame(pd.date_range('2021-03-01' , dt.datetime.today()), columns= ['date' ])= time_encoding(tdf.date, freq= freq)
for freq in ['microsecond' , 'second' , 'minute' , 'hour' , 'day' , 'dayofweek' , 'dayofyear' , 'month' ]:= pd.date_range('2021-03-01' , dt.datetime.today())= time_encoding(dateindex, freq= freq)
= time_encoding(date_df['date' ], 'dayofweek' )'DayOfWeek' )'dow_sin' ] = dow_sin'dow_cos' ] = dow_cos
0
2021-05-01 00:00:00
0
0.773597
0.465634
-0.974928
-0.222521
1
2021-05-01 04:00:00
0
0.265526
0.963753
-0.974928
-0.222521
2
2021-05-01 08:00:00
0
0.448508
0.953596
-0.974928
-0.222521
3
2021-05-01 12:00:00
0
0.868802
0.526845
-0.974928
-0.222521
4
2021-05-01 16:00:00
0
0.223070
0.304842
-0.974928
-0.222521
5
2021-05-01 20:00:00
0
0.645661
0.270956
-0.974928
-0.222521
6
2021-05-01 00:00:00
1
0.017250
0.787757
-0.974928
-0.222521
7
2021-05-01 04:00:00
1
0.783341
0.608269
-0.974928
-0.222521
8
2021-05-01 08:00:00
1
0.629875
0.170726
-0.974928
-0.222521
9
2021-05-01 12:00:00
1
0.302927
0.682136
-0.974928
-0.222521
10
2021-05-01 16:00:00
1
0.426247
0.926149
-0.974928
-0.222521
11
2021-05-01 20:00:00
1
0.830624
0.543715
-0.974928
-0.222521
source
get_gaps
get_gaps (o:torch.Tensor, forward:bool=True, backward:bool=True,
nearest:bool=True, normalize:bool=True)
Number of sequence steps from previous, to next and/or to nearest real value along the last dimension of 3D arrays or tensors
source
nearest_gaps
nearest_gaps (o, normalize=True)
Number of sequence steps to nearest real value along the last dimension of 3D arrays or tensors
source
backward_gaps
backward_gaps (o, normalize=True)
Number of sequence steps to next real value along the last dimension of 3D arrays or tensors
source
forward_gaps
forward_gaps (o, normalize=True)
Number of sequence steps since previous real value along the last dimension of 3D arrays or tensors
= torch.rand(1 , 2 , 8 )= t.numpy()< .6 ] = np.nanmin ().item(), 0 )min (), 0 )min ().item(), 1 )min (), 1 )sum (), 0 )sum (), 0 )= get_gaps(t)1 ,6 ,8 ))sum (), 0 )
source
add_delta_timestamp_cols
add_delta_timestamp_cols (df, cols=None, groupby=None, forward=True,
backward=True, nearest=True, normalize=True)
# Add delta timestamp features for the no groups setting = pd.date_range('2021-05-01' , '2021-05-07' ).values= np.zeros((len (dates), 2 ))0 ] = dates1 ] = np.random.rand(len (dates))= ['date' , 'feature1' ]= pd.DataFrame(data, columns= cols).astype({'date' : 'datetime64[ns]' , 'feature1' : float })1 ,3 ,4 ],'feature1' ] = np.nan
0
2021-05-01
0.132532
1
2021-05-02
NaN
2
2021-05-03
0.403176
3
2021-05-04
NaN
4
2021-05-05
NaN
5
2021-05-06
0.179554
6
2021-05-07
0.446536
# No groups = date_df.copy()'feature1_dt_fwd' ] = np.array([1 ,1 ,2 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,1 ])'feature1_dt_bwd' ] = np.array([2 ,1 ,3 ,2 ,1 ,1 ,1 ])'feature1_dt_nearest' ] = np.array([1 ,1 ,2 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,1 ])= add_delta_timestamp_cols(date_df, cols= 'feature1' , normalize= False )
0
2021-05-01
0.132532
1
2
1
1
2021-05-02
NaN
1
1
1
2
2021-05-03
0.403176
2
3
2
3
2021-05-04
NaN
1
2
1
4
2021-05-05
NaN
2
1
1
5
2021-05-06
0.179554
3
1
1
6
2021-05-07
0.446536
1
1
1
# Add delta timestamp features within a group = pd.date_range('2021-05-01' , '2021-05-07' ).values= np.concatenate((dates, dates))= np.zeros((len (dates), 3 ))0 ] = dates1 ] = np.array([0 ]* (len (dates)// 2 )+ [1 ]* (len (dates)// 2 ))2 ] = np.random.rand(len (dates))= ['date' , 'id' , 'feature1' ]= pd.DataFrame(data, columns= cols).astype({'date' : 'datetime64[ns]' , 'id' : int , 'feature1' : float })1 ,3 ,4 ,8 ,9 ,11 ],'feature1' ] = np.nan
0
2021-05-01
0
0.405327
1
2021-05-02
0
NaN
2
2021-05-03
0
0.055934
3
2021-05-04
0
NaN
4
2021-05-05
0
NaN
5
2021-05-06
0
0.698408
6
2021-05-07
0
0.064831
7
2021-05-01
1
0.407541
8
2021-05-02
1
NaN
9
2021-05-03
1
NaN
10
2021-05-04
1
0.113590
11
2021-05-05
1
NaN
12
2021-05-06
1
0.548088
13
2021-05-07
1
0.348813
# groupby='id' = date_df.copy()'feature1_dt_fwd' ] = np.array([1 ,1 ,2 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,2 ,1 ])'feature1_dt_bwd' ] = np.array([2 ,1 ,3 ,2 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,3 ,2 ,1 ,2 ,1 ,1 ,1 ])'feature1_dt_nearest' ] = np.array([1 ,1 ,2 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,2 ,1 ,1 ,1 ])= add_delta_timestamp_cols(date_df, cols= 'feature1' , groupby= 'id' , normalize= False )
0
2021-05-01
0
0.405327
1
2
1
1
2021-05-02
0
NaN
1
1
1
2
2021-05-03
0
0.055934
2
3
2
3
2021-05-04
0
NaN
1
2
1
4
2021-05-05
0
NaN
2
1
1
5
2021-05-06
0
0.698408
3
1
1
6
2021-05-07
0
0.064831
1
1
1
7
2021-05-01
1
0.407541
1
3
1
8
2021-05-02
1
NaN
1
2
1
9
2021-05-03
1
NaN
2
1
1
10
2021-05-04
1
0.113590
3
2
2
11
2021-05-05
1
NaN
1
1
1
12
2021-05-06
1
0.548088
2
1
1
13
2021-05-07
1
0.348813
1
1
1
SlidingWindow and SlidingWindowPanel are 2 useful functions that will allow you to create an array with segments of a pandas dataframe based on multiple criteria.
source
SlidingWindow
SlidingWindow (window_len:int, stride:Optional[int]=1, start:int=0,
pad_remainder:bool=False, padding:str='post',
padding_value:float=nan, add_padding_feature:bool=True,
get_x:Union[NoneType,int,list]=None,
get_y:Union[NoneType,int,list]=None,
y_func:Optional[<built-infunctioncallable>]=None,
output_processor:Optional[<built-
infunctioncallable>]=None, copy:bool=False,
horizon:Union[int,list]=1, seq_first:bool=True,
sort_by:Optional[list]=None, ascending:bool=True,
check_leakage:bool=True)
*Applies a sliding window to a 1d or 2d input (np.ndarray, torch.Tensor or pd.DataFrame)
Input:
You can use np.ndarray, pd.DataFrame or torch.Tensor as input
shape: (seq_len, ) or (seq_len, n_vars) if seq_first=True else (n_vars, seq_len)*
window_len
int
length of lookback window
stride
Optional
1
n datapoints the window is moved ahead along the sequence. Default: 1. If None, stride=window_len (no overlap)
start
int
0
determines the step where the first window is applied: 0 (default) or a given step (int). Previous steps will be discarded.
pad_remainder
bool
False
allows to pad remainder subsequences when the sliding window is applied and get_y == [] (unlabeled data).
padding
str
post
‘pre’ or ‘post’ (optional, defaults to ‘pre’): pad either before or after each sequence. If pad_remainder == False, it indicates the starting point to create the sequence (‘pre’ from the end, and ‘post’ from the beginning)
padding_value
float
nan
value (float) that will be used for padding. Default: np.nan
add_padding_feature
bool
True
add an additional feature indicating whether each timestep is padded (1) or not (0).
get_x
Union
None
indices of columns that contain the independent variable (xs). If None, all data will be used as x.
get_y
Union
None
indices of columns that contain the target (ys). If None, all data will be used as y. [] means no y data is created (unlabeled data).
y_func
Optional
None
optional function to calculate the ys based on the get_y col/s and each y sub-window. y_func must be a function applied to axis=1!
output_processor
Optional
None
optional function to process the final output (X (and y if available)). This is useful when some values need to be removed.The function should take X and y (even if it’s None) as arguments.
copy
bool
False
copy the original object to avoid changes in it.
horizon
Union
1
number of future datapoints to predict (y). If get_y is [] horizon will be set to 0.
seq_first
bool
True
True if input shape (seq_len, n_vars), False if input shape (n_vars, seq_len)
sort_by
Optional
None
column/s used for sorting the array in ascending order
ascending
bool
True
used in sorting
check_leakage
bool
True
checks if there’s leakage in the output between X and y
= 5 = 5 = np.repeat(np.arange(13 ).reshape(- 1 ,1 ), 3 , axis=- 1 )print ('input shape:' , t.shape)= SlidingWindow(wl, stride= stride, pad_remainder= True , get_y= [])(t)
array([[[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4.],
[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4.],
[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]],
[[ 5., 6., 7., 8., 9.],
[ 5., 6., 7., 8., 9.],
[ 5., 6., 7., 8., 9.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]],
[[10., 11., 12., nan, nan],
[10., 11., 12., nan, nan],
[10., 11., 12., nan, nan],
[ 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.]]])
= 5 = np.arange(10 )print ('input shape:' , t.shape)= SlidingWindow(wl)(t)1 :], (1 , wl))
(#5) [(array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]),),(array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]]),),(array([[2, 3, 4, 5, 6]]),),(array([[3, 4, 5, 6, 7]]),),(array([[4, 5, 6, 7, 8]]),)]
= 5 = 1 = np.arange(10 )print ('input shape:' , t.shape)= SlidingWindow(wl, stride= 1 , horizon= h)(t)= itemify(X, y)print (items)0 ][0 ].shape, (1 , wl))0 ][1 ].shape, ())
input shape: (10,)
[(array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]), 5), (array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]]), 6), (array([[2, 3, 4, 5, 6]]), 7), (array([[3, 4, 5, 6, 7]]), 8), (array([[4, 5, 6, 7, 8]]), 9)]
= 5 = 2 # 2 or more = np.arange(10 )print ('input shape:' , t.shape)= SlidingWindow(wl, horizon= h)(t)= itemify(X, y)print (items)0 ][0 ].shape, (1 , wl))0 ][1 ].shape, (2 , ))
input shape: (10,)
[(array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]), array([5, 6])), (array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]]), array([6, 7])), (array([[2, 3, 4, 5, 6]]), array([7, 8])), (array([[3, 4, 5, 6, 7]]), array([8, 9]))]
= 5 = 2 # 2 or more = np.arange(10 ).reshape(1 , - 1 )print ('input shape:' , t.shape)= SlidingWindow(wl, stride= 1 , horizon= h, get_y= None , seq_first= False )(t)= itemify(X, y)print (items)0 ][0 ].shape, (1 , wl))0 ][1 ].shape, (2 , ))
input shape: (1, 10)
[(array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]), array([5, 6])), (array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]]), array([6, 7])), (array([[2, 3, 4, 5, 6]]), array([7, 8])), (array([[3, 4, 5, 6, 7]]), array([8, 9]))]
= 5 = 2 # 2 or more = np.arange(10 ).reshape(1 , - 1 )print ('input shape:' , t.shape)= SlidingWindow(wl, stride= 1 , horizon= h, seq_first= False )(t)= itemify(X, y)print (items)0 ][0 ].shape, (1 , wl))
input shape: (1, 10)
[(array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]), array([5, 6])), (array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]]), array([6, 7])), (array([[2, 3, 4, 5, 6]]), array([7, 8])), (array([[3, 4, 5, 6, 7]]), array([8, 9]))]
= 5 = np.arange(10 ).reshape(1 , - 1 )print ('input shape:' , t.shape)= SlidingWindow(wl, stride= 3 , horizon= 1 , get_y= None , seq_first= False )(t)= itemify(X, y)print (items)0 ][0 ].shape, (1 , wl))0 ][1 ].shape, ())
input shape: (1, 10)
[(array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]), 5), (array([[3, 4, 5, 6, 7]]), 8)]
= 5 = 3 = np.arange(20 )print ('input shape:' , t.shape)= SlidingWindow(wl, stride= None , horizon= 1 , start= start)(t)= itemify(X, y)print (items)0 ][0 ].shape, (1 , wl))0 ][1 ].shape, ())
input shape: (20,)
[(array([[3, 4, 5, 6, 7]]), 8), (array([[ 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]]), 13), (array([[13, 14, 15, 16, 17]]), 18)]
= 5 = np.arange(20 )print ('input shape:' , t.shape)= pd.DataFrame(t, columns= ['var' ])= SlidingWindow(wl, stride= None , horizon= 1 , get_y= None )(df)= itemify(X, y)print (items)0 ][0 ].shape, (1 , wl))0 ][1 ].shape, ())
0
0
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
7
7
8
8
9
9
10
10
11
11
12
12
13
13
14
14
15
15
16
16
17
17
18
18
19
19
[(array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]), 5), (array([[5, 6, 7, 8, 9]]), 10), (array([[10, 11, 12, 13, 14]]), 15)]
= 5 = np.arange(20 )print ('input shape:' , t.shape)= pd.DataFrame(t, columns= ['var' ])= SlidingWindow(wl, stride= 1 , horizon= 1 , get_y= None )(df)= itemify(X, y)print (items)0 ][0 ].shape, (1 , wl))0 ][1 ].shape, ())
0
0
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
7
7
8
8
9
9
10
10
11
11
12
12
13
13
14
14
15
15
16
16
17
17
18
18
19
19
[(array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]), 5), (array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]]), 6), (array([[2, 3, 4, 5, 6]]), 7), (array([[3, 4, 5, 6, 7]]), 8), (array([[4, 5, 6, 7, 8]]), 9), (array([[5, 6, 7, 8, 9]]), 10), (array([[ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]]), 11), (array([[ 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]]), 12), (array([[ 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]]), 13), (array([[ 9, 10, 11, 12, 13]]), 14), (array([[10, 11, 12, 13, 14]]), 15), (array([[11, 12, 13, 14, 15]]), 16), (array([[12, 13, 14, 15, 16]]), 17), (array([[13, 14, 15, 16, 17]]), 18), (array([[14, 15, 16, 17, 18]]), 19)]
= 5 = np.arange(20 )print ('input shape:' , t.shape)= pd.DataFrame(t, columns= ['var' ]).T= SlidingWindow(wl, stride= None , horizon= 1 , get_y= None , seq_first= False )(df)= itemify(X, y)print (items)0 ][0 ].shape, (1 , wl))0 ][1 ].shape, ())
var
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
[(array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]), 5), (array([[5, 6, 7, 8, 9]]), 10), (array([[10, 11, 12, 13, 14]]), 15)]
= 5 = 3 = (torch.stack(n_vars * [torch.arange(10 )]).T * tensor([1 , 10 , 100 ]))print ('input shape:' , t.shape)= pd.DataFrame(t, columns= [f'var_ { i} ' for i in range (n_vars)])= SlidingWindow(wl, horizon= 1 )(df)= itemify(X, y)print (items)0 ][0 ].shape, (n_vars, wl))
input shape: torch.Size([10, 3])
0
0
0
0
1
1
10
100
2
2
20
200
3
3
30
300
4
4
40
400
5
5
50
500
6
6
60
600
7
7
70
700
8
8
80
800
9
9
90
900
[(array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 0, 10, 20, 30, 40],
[ 0, 100, 200, 300, 400]]), array([ 5, 50, 500])), (array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 10, 20, 30, 40, 50],
[100, 200, 300, 400, 500]]), array([ 6, 60, 600])), (array([[ 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[ 20, 30, 40, 50, 60],
[200, 300, 400, 500, 600]]), array([ 7, 70, 700])), (array([[ 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 30, 40, 50, 60, 70],
[300, 400, 500, 600, 700]]), array([ 8, 80, 800])), (array([[ 4, 5, 6, 7, 8],
[ 40, 50, 60, 70, 80],
[400, 500, 600, 700, 800]]), array([ 9, 90, 900]))]
= 5 = 3 = (torch.stack(n_vars * [torch.arange(10 )]).T * tensor([1 , 10 , 100 ]))print ('input shape:' , t.shape)= pd.DataFrame(t, columns= [f'var_ { i} ' for i in range (n_vars)])= SlidingWindow(wl, horizon= 1 , get_y= "var_0" )(df)= itemify(X, y)print (items)0 ][0 ].shape, (n_vars, wl))
input shape: torch.Size([10, 3])
0
0
0
0
1
1
10
100
2
2
20
200
3
3
30
300
4
4
40
400
5
5
50
500
6
6
60
600
7
7
70
700
8
8
80
800
9
9
90
900
[(array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 0, 10, 20, 30, 40],
[ 0, 100, 200, 300, 400]]), 5), (array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 10, 20, 30, 40, 50],
[100, 200, 300, 400, 500]]), 6), (array([[ 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[ 20, 30, 40, 50, 60],
[200, 300, 400, 500, 600]]), 7), (array([[ 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 30, 40, 50, 60, 70],
[300, 400, 500, 600, 700]]), 8), (array([[ 4, 5, 6, 7, 8],
[ 40, 50, 60, 70, 80],
[400, 500, 600, 700, 800]]), 9)]
= 5 = 3 = (torch.stack(n_vars * [torch.arange(10 )]).T * tensor([1 , 10 , 100 ]))print ('input shape:' , t.shape)= [f'var_ { i} ' for i in range (n_vars- 1 )]+ ['target' ]= pd.DataFrame(t, columns= columns)= SlidingWindow(wl, horizon= 1 , get_x= columns[:- 1 ], get_y= 'target' )(df)= itemify(X, y)print (items)0 ][0 ].shape, (n_vars- 1 , wl))0 ][1 ].shape, ())
input shape: torch.Size([10, 3])
0
0
0
0
1
1
10
100
2
2
20
200
3
3
30
300
4
4
40
400
5
5
50
500
6
6
60
600
7
7
70
700
8
8
80
800
9
9
90
900
[(array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 0, 10, 20, 30, 40]]), 500), (array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
[10, 20, 30, 40, 50]]), 600), (array([[ 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[20, 30, 40, 50, 60]]), 700), (array([[ 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
[30, 40, 50, 60, 70]]), 800), (array([[ 4, 5, 6, 7, 8],
[40, 50, 60, 70, 80]]), 900)]
= 3 = (np.random.rand(1000 , n_vars) - .5 ).cumsum(0 )print (t.shape)= SlidingWindow(5 , stride= None , horizon= 0 , get_x= [0 ,1 ], get_y= 2 )(t)0 ].shape, (n_vars- 1 , wl))0 ].shape, ())print (X.shape, y.shape)
= 5 = 3 = (np.random.rand(100 , n_vars) - .5 ).cumsum(0 )print (t.shape)= [f'var_ { i} ' for i in range (n_vars- 1 )]+ ['target' ]= pd.DataFrame(t, columns= columns)= SlidingWindow(5 , horizon= 0 , get_x= columns[:- 1 ], get_y= 'target' )(df)0 ].shape, (n_vars- 1 , wl))0 ].shape, ())print (X.shape, y.shape)
0
0.154072
0.197194
-0.083179
1
0.402744
-0.248788
-0.560573
2
0.448209
0.224215
-0.681264
3
0.631502
0.406760
-1.162043
4
1.099973
0.179926
-0.712690
...
...
...
...
95
-0.405079
3.662311
-2.779159
96
-0.445625
3.488809
-2.663381
97
-0.187349
3.304898
-2.695971
98
-0.100652
3.505663
-2.590652
99
0.371272
3.279901
-2.764369
100 rows × 3 columns
= 100 = 5 = (np.random.rand(seq_len, n_vars) - .5 ).cumsum(0 )print (t.shape)= [f'var_ { i} ' for i in range (n_vars- 1 )]+ ['target' ]= pd.DataFrame(t, columns= columns)= SlidingWindow(5 , stride= 1 , horizon= 0 , get_x= columns[:- 1 ], get_y= 'target' , seq_first= True )(df)0 ].shape, (n_vars- 1 , wl))0 ].shape, ())print (X.shape, y.shape)
0
0.443639
-0.288128
-0.049732
0.288915
0.325872
1
-0.047608
-0.009738
0.056768
0.541395
0.017496
2
-0.243972
0.102227
0.361387
0.628397
0.049012
3
-0.721266
0.045104
0.724062
0.940693
0.510875
4
-0.641269
0.141927
0.793837
1.158903
0.417040
...
...
...
...
...
...
95
3.488117
2.345512
0.745483
0.258568
2.468550
96
3.187006
1.945844
0.833228
0.511198
2.115330
97
3.019862
1.739802
0.488732
0.881324
2.387837
98
3.314247
1.992000
0.119230
0.797794
2.327720
99
3.394578
2.012458
0.003244
0.387125
2.345970
100 rows × 5 columns
= 100 = 5 = (np.random.rand(seq_len, n_vars) - .5 ).cumsum(0 )print (t.shape)= [f'var_ { i} ' for i in range (n_vars- 1 )] + ['target' ]= pd.DataFrame(t, columns= columns).T= SlidingWindow(5 , stride= 1 , horizon= 0 , get_x= columns[:- 1 ], get_y= 'target' , seq_first= False )(df)0 ].shape, (n_vars- 1 , wl))0 ].shape, ())print (X.shape, y.shape)
var_0
-0.407162
-0.742169
-1.193053
-1.058644
-0.721243
-1.056788
-1.316226
-1.247859
-1.391482
-1.258618
...
-2.847911
-3.118643
-3.444248
-3.036050
-2.664068
-2.473782
-2.508080
-2.878210
-2.841170
-2.688932
var_1
0.111643
-0.286318
-0.221917
-0.026094
-0.332200
-0.376518
-0.144763
0.225361
0.487134
0.435856
...
1.569158
1.294548
1.564455
1.501243
1.490928
1.450602
1.440730
1.755607
1.380986
1.236284
var_2
-0.126951
-0.484267
-0.480375
-0.706987
-0.571379
-0.561959
-0.717696
-0.586035
-0.298053
-0.047405
...
-1.748096
-1.508691
-1.158258
-1.116485
-1.153738
-1.575450
-1.875091
-1.613255
-1.274859
-1.592096
var_3
-0.462238
-0.748774
-0.625473
-0.360442
-0.789178
-0.530832
-0.785290
-0.413452
0.083685
-0.110964
...
-4.873450
-4.382297
-4.531454
-4.087051
-4.087801
-4.391084
-4.262526
-4.650170
-4.465874
-4.535273
target
0.241454
0.084139
-0.012974
0.096328
0.501035
0.697043
0.229185
0.497430
0.552922
0.218345
...
-4.582426
-4.194067
-3.785398
-3.808516
-3.629740
-3.398645
-3.828007
-3.600028
-3.614195
-3.592783
5 rows × 100 columns
= 100 = 5 = (np.random.rand(seq_len, n_vars) - .5 ).cumsum(0 )print (t.shape)= [f'var_ { i} ' for i in range (n_vars- 1 )] + ['target' ]= pd.DataFrame(t, columns= columns).T= SlidingWindow(5 , stride= None , horizon= 0 , get_x= columns[:- 1 ], get_y= 'target' , seq_first= False )(df)0 ].shape, (n_vars- 1 , wl))0 ].shape, ())print (X.shape, y.shape)
var_0
0.210943
-0.264863
-0.307942
0.176782
-0.188244
0.118824
0.593353
0.611408
0.176396
0.566034
...
-4.738294
-5.138743
-5.203979
-4.835758
-4.534974
-4.310112
-4.366365
-4.328250
-4.527717
-4.432726
var_1
-0.086375
-0.457413
0.025571
0.428256
0.611573
0.319714
-0.085129
0.161735
0.052730
-0.356617
...
7.203539
7.300534
7.267954
6.838923
7.054134
6.612532
7.108269
6.966000
7.407915
7.332567
var_2
0.166139
-0.231839
-0.468804
-0.565628
-0.500941
-0.706951
-0.881385
-1.138549
-0.978276
-0.952727
...
0.391942
0.802356
0.395688
0.033288
0.147283
0.589911
0.360847
0.322019
0.478120
0.278228
var_3
-0.234297
-0.467480
-0.925036
-0.572783
-0.345585
0.149537
-0.078098
-0.577732
-0.771975
-0.322283
...
-1.487032
-1.971348
-2.300616
-2.767312
-2.657974
-2.880908
-2.567235
-2.758240
-2.605518
-2.166444
target
-0.416187
-0.164800
-0.283554
-0.534897
-0.896808
-0.456572
-0.889556
-1.178456
-0.877891
-1.176442
...
-6.094650
-6.510793
-6.408799
-6.685696
-6.672726
-6.210781
-6.377436
-5.974001
-5.755187
-5.608240
5 rows × 100 columns
from tsai.data.validation import TrainValidTestSplitter
= 100 = 5 = (np.random.rand(seq_len, n_vars) - .5 ).cumsum(0 )print (t.shape)= [f'var_ { i} ' for i in range (n_vars- 1 )]+ ['target' ]= pd.DataFrame(t, columns= columns)= SlidingWindow(5 , stride= 1 , horizon= 0 , get_x= columns[:- 1 ], get_y= 'target' , seq_first= True )(df)= TrainValidTestSplitter(valid_size= .2 , shuffle= False )(y)
0
0.123248
-0.081596
0.099444
0.447980
-0.397975
1
0.469671
-0.334499
0.307867
0.141345
-0.131085
2
0.522902
-0.696817
0.386597
0.156818
0.128043
3
0.487025
-0.966153
-0.050574
-0.248479
-0.088962
4
0.396284
-1.319821
-0.113121
-0.379227
0.313690
...
...
...
...
...
...
95
6.138836
-1.602917
1.713049
1.421797
-1.873899
96
5.892472
-1.896914
1.401137
1.065859
-2.239942
97
5.421917
-1.728568
1.481270
0.998533
-2.157474
98
5.763120
-1.404330
1.931361
1.295956
-1.934397
99
5.827842
-1.762438
1.831712
1.014259
-1.831573
100 rows × 5 columns
((96, 4, 5),
(96,),
((#77) [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9...], (#19) [77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86...]))
= np.concatenate([np.linspace(0 , 1 , 11 ).reshape(- 1 ,1 ).repeat(2 , 1 ), np.arange(11 ).reshape(- 1 ,1 )], - 1 )= pd.DataFrame(data, columns= ['col1' , 'col2' , 'target' ])'target' ] = df_test['target' ].astype(int )
0
0.0
0.0
0
1
0.1
0.1
1
2
0.2
0.2
2
3
0.3
0.3
3
4
0.4
0.4
4
5
0.5
0.5
5
6
0.6
0.6
6
7
0.7
0.7
7
8
0.8
0.8
8
9
0.9
0.9
9
10
1.0
1.0
10
def _y_func(o): return o[:, 0 ]
for wl in np.arange(1 , 20 ):= SlidingWindow(wl, None , pad_remainder= True , get_x= ['col1' , 'col2' ], get_y= ['target' ], horizon=- wl, y_func= _y_func)(df_test)0 ], math.ceil((len (df_test))/ wl))0 ], y.shape[0 ])2 ], wl)0 , 0 ]* 10 , y)
for wl in np.arange(1 , 20 ):= SlidingWindow(wl, None , pad_remainder= True , get_x= ['col1' , 'col2' ], get_y= ['target' ], horizon=- wl, y_func= None )(df_test)0 ], math.ceil((len (df_test))/ wl))0 ], y.shape[0 ])2 ], wl)
for wl in np.arange(1 , len (df_test)+ 1 ):= SlidingWindow(wl, None , pad_remainder= False , get_x= ['col1' , 'col2' ], get_y= ['target' ], horizon=- wl, y_func= None )(df_test)0 ], len (df_test) // wl)0 ], y.shape[0 ])2 ], wl)
for wl in np.arange(1 , 20 ):= SlidingWindow(wl, None , pad_remainder= True , get_x= ['col1' , 'col2' ], get_y= [], horizon= 0 )(df_test)0 ], math.ceil((len (df_test))/ wl))2 ], wl)
for wl in np.arange(2 , len (df_test)):= SlidingWindow(wl, wl, pad_remainder= False , get_x= ['col1' , 'col2' ], get_y= [], horizon= 0 )(df_test)0 ], len (df_test) // wl)2 ], wl)
= pd.DataFrame()'sample_id' ] = np.concatenate([np.ones(n)* (i + 1 ) for i,n in enumerate ([13 ])])'var1' ] = df['sample_id' ] + df.index.values - 1 'var2' ] = df['var1' ] * 10 'target' ] = (df['var1' ]).astype(int )'sample_id' ] = df['sample_id' ].astype(int )
0
1
0.0
0.0
0
1
1
1.0
10.0
1
2
1
2.0
20.0
2
3
1
3.0
30.0
3
4
1
4.0
40.0
4
5
1
5.0
50.0
5
6
1
6.0
60.0
6
7
1
7.0
70.0
7
8
1
8.0
80.0
8
9
1
9.0
90.0
9
10
1
10.0
100.0
10
11
1
11.0
110.0
11
12
1
12.0
120.0
12
= SlidingWindow(window_len= 3 , stride= 2 , start= 3 , pad_remainder= False , padding= "pre" , padding_value= np.nan, add_padding_feature= False ,= ["var1" , "var2" ], get_y= ["target" ], y_func= None , output_processor= None , copy= False , horizon= 4 , seq_first= True , sort_by= None ,= True , check_leakage= True )(df)2 , 2 , 3 ))2 , 4 ))
(array([[[ 4., 5., 6.],
[40., 50., 60.]],
[[ 6., 7., 8.],
[60., 70., 80.]]]),
array([[ 7, 8, 9, 10],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12]]))
= SlidingWindow(window_len= 3 , stride= 2 , start= 3 , pad_remainder= True , padding= "pre" , padding_value= np.nan, add_padding_feature= False ,= ["var1" , "var2" ], get_y= ["target" ], y_func= None , output_processor= None , copy= False , horizon= 4 , seq_first= True , sort_by= None ,= True , check_leakage= True )(df)3 , 2 , 3 ))3 , 4 ))
(array([[[nan, 3., 4.],
[nan, 30., 40.]],
[[ 4., 5., 6.],
[40., 50., 60.]],
[[ 6., 7., 8.],
[60., 70., 80.]]]),
array([[ 5, 6, 7, 8],
[ 7, 8, 9, 10],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12]]))
= SlidingWindow(window_len= 3 , stride= 2 , start= 3 , pad_remainder= False , padding= "post" , padding_value= np.nan, add_padding_feature= False ,= ["var1" , "var2" ], get_y= ["target" ], y_func= None , output_processor= None , copy= False , horizon= 4 , seq_first= True , sort_by= None ,= True , check_leakage= True )(df)2 , 2 , 3 ))2 , 4 ))
(array([[[ 3., 4., 5.],
[30., 40., 50.]],
[[ 5., 6., 7.],
[50., 60., 70.]]]),
array([[ 6, 7, 8, 9],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]]))
= SlidingWindow(window_len= 3 , stride= 2 , start= 3 , pad_remainder= True , padding= "post" , padding_value= np.nan, add_padding_feature= False ,= ["var1" , "var2" ], get_y= ["target" ], y_func= None , output_processor= None , copy= False , horizon= 4 , seq_first= True , sort_by= None ,= True , check_leakage= True )(df)3 , 2 , 3 ))3 , 4 ))
(array([[[ 3., 4., 5.],
[30., 40., 50.]],
[[ 5., 6., 7.],
[50., 60., 70.]],
[[ 7., 8., 9.],
[70., 80., 90.]]]),
array([[ 6., 7., 8., 9.],
[ 8., 9., 10., 11.],
[10., 11., 12., nan]]))
= SlidingWindow(window_len= 10 , stride= 2 , start= 3 , pad_remainder= True , padding= "pre" , padding_value= np.nan, add_padding_feature= False ,= ["var1" , "var2" ], get_y= ["target" ], y_func= None , output_processor= None , copy= False , horizon= 4 , seq_first= True , sort_by= None ,= True , check_leakage= True )(df)1 , 2 , 10 ))1 , 4 ))
(array([[[nan, nan, nan, nan, 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8.],
[nan, nan, nan, nan, 30., 40., 50., 60., 70., 80.]]]),
array([[ 9, 10, 11, 12]]))
= SlidingWindow(window_len= 10 , stride= 2 , start= 3 , pad_remainder= True , padding= "post" , padding_value= np.nan, add_padding_feature= False ,= ["var1" , "var2" ], get_y= ["target" ], y_func= None , output_processor= None , copy= False , horizon= 4 , seq_first= True , sort_by= None ,= True , check_leakage= True )(df)1 , 2 , 10 ))1 , 4 ))
(array([[[ 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12.],
[ 30., 40., 50., 60., 70., 80., 90., 100., 110., 120.]]]),
array([[nan, nan, nan, nan]]))
source
SlidingWindowPanel
SlidingWindowPanel (window_len:int, unique_id_cols:list,
stride:Optional[int]=1, start:int=0,
pad_remainder:bool=False, padding:str='post',
padding_value:float=nan,
add_padding_feature:bool=True,
get_x:Union[NoneType,int,list]=None,
get_y:Union[NoneType,int,list]=None,
y_func:Optional[<built-infunctioncallable>]=None,
output_processor:Optional[<built-
infunctioncallable>]=None, copy:bool=False,
horizon:Union[int,list]=1, seq_first:bool=True,
sort_by:Optional[list]=None, ascending:bool=True,
check_leakage:bool=True, return_key:bool=False,
verbose:bool=True)
*Applies a sliding window to a pd.DataFrame.
Args: window_len = length of lookback window unique_id_cols = pd.DataFrame columns that will be used to identify a time series for each entity. stride = n datapoints the window is moved ahead along the sequence. Default: 1. If None, stride=window_len (no overlap) start = determines the step where the first window is applied: 0 (default), a given step (int), or random within the 1st stride (None). pad_remainder = allows to pad remainder subsequences when the sliding window is applied and get_y == [] (unlabeled data). padding = ‘pre’ or ‘post’ (optional, defaults to ‘pre’): pad either before or after each sequence. If pad_remainder == False, it indicates the starting point to create the sequence (‘pre’ from the end, and ‘post’ from the beginning) padding_value = value (float) that will be used for padding. Default: np.nan add_padding_feature = add an additional feature indicating whether each timestep is padded (1) or not (0). horizon = number of future datapoints to predict (y). If get_y is [] horizon will be set to 0. * 0 for last step in each sub-window. * n > 0 for a range of n future steps (1 to n). * n < 0 for a range of n past steps (-n + 1 to 0). * list : for those exact timesteps. get_x = indices of columns that contain the independent variable (xs). If None, all data will be used as x. get_y = indices of columns that contain the target (ys). If None, all data will be used as y. [] means no y data is created (unlabeled data). y_func = function to calculate the ys based on the get_y col/s and each y sub-window. y_func must be a function applied to axis=1! output_processor = optional function to filter output (X (and y if available)). This is useful when some values need to be removed. The function should take X and y (even if it’s None) as arguments. copy = copy the original object to avoid changes in it. seq_first = True if input shape (seq_len, n_vars), False if input shape (n_vars, seq_len) sort_by = column/s used for sorting the array in ascending order ascending = used in sorting check_leakage = checks if there’s leakage in the output between X and y return_key = when True, the key corresponsing to unique_id_cols for each sample is returned verbose = controls verbosity. True or 1 displays progress bar. 2 or more show records that cannot be created due to its length.
Input: You can use np.ndarray, pd.DataFrame or torch.Tensor as input shape: (seq_len, ) or (seq_len, n_vars) if seq_first=True else (n_vars, seq_len)*
= 100_000 = 5 = 10 = (torch.stack(n_vars * [torch.arange(samples)]).T * tensor([10 ** i for i in range (n_vars)]))= pd.DataFrame(t, columns= [f'var_ { i} ' for i in range (n_vars)])'time' ] = np.arange(len (t))'device' ] = 0 'target' ] = np.random.randint(0 , 2 , len (df))= df.copy()= df.copy()= ['var_0' , 'var_1' , 'var_2' , 'device' , 'target' ]= df2[cols] + 1 = df3[cols] + 2 = df2.loc[:3 ]'region' ] = 'A' 'region' ] = 'A' 'region' ] = 'B' = pd.concat([df, df2, df3], ignore_index= True )'index' ] = np.arange(len (df))= df.sample(frac= 1 ).reset_index(drop= True )
0
86008
860080
8600800
86008000
860080000
8600800000
86008000000
860080000000
8600800000000
86008000000000
86008
0
0
A
86008
1
90003
900012
9000102
90001000
900010000
9000100000
90001000000
900010000000
9000100000000
90001000000000
90001
2
2
B
190005
2
43819
438172
4381702
43817000
438170000
4381700000
43817000000
438170000000
4381700000000
43817000000000
43817
2
3
B
143821
3
80751
807492
8074902
80749000
807490000
8074900000
80749000000
807490000000
8074900000000
80749000000000
80749
2
3
B
180753
4
84917
849152
8491502
84915000
849150000
8491500000
84915000000
849150000000
8491500000000
84915000000000
84915
2
3
B
184919
= SlidingWindowPanel(window_len= 5 , unique_id_cols= ['device' ], stride= 1 , start= 0 , get_x= df.columns[:n_vars], get_y= ['target' ], = 0 , seq_first= True , sort_by= ['time' ], ascending= True , return_key= False )(df)
...data processed
concatenating X...
...X concatenated
concatenating y...
...y concatenated
((199992, 10, 5), (199992,))
= SlidingWindowPanel(window_len= 5 , unique_id_cols= ['device' ], stride= 1 , start= 0 , get_x= df.columns[:n_vars], get_y= ['target' ], = 0 , seq_first= True , sort_by= ['time' ], ascending= True , return_key= True )(df)
...data processed
concatenating X...
...X concatenated
concatenating y...
...y concatenated
((199992, 10, 5), (199992,), (199992,))
= SlidingWindowPanel(window_len= 5 , unique_id_cols= ['device' , 'region' ], stride= 1 , start= 0 , get_x= df.columns[:n_vars], get_y= ['target' ], = 0 , seq_first= True , sort_by= ['time' ], ascending= True )(df)
...data processed
concatenating X...
...X concatenated
concatenating y...
...y concatenated
((199992, 10, 5), (199992,))
# y_func must be a function applied to axis=1! def y_max(o): return np.max (o, axis= 1 )
= SlidingWindowPanel(window_len= 5 , unique_id_cols= ['device' , 'region' ], stride= 1 , start= 0 , get_x= df.columns[:n_vars], get_y= ['target' ], = y_max, horizon= 5 , seq_first= True , sort_by= ['time' ], ascending= True )(df)
...data processed
concatenating X...
...X concatenated
concatenating y...
...y concatenated
((199982, 10, 5), (199982,))
source
identify_padding
identify_padding (float_mask, value=-1)
*Identifies padded subsequences in a mask of type float
This function identifies as padded subsequences those where all values == nan from the end of the sequence (last dimension) across all channels, and sets those values to the selected value (default = -1)
Args: mask: boolean or float mask value: scalar that will be used to identify padded subsequences*
= 5 = 5 = np.repeat(np.arange(13 ).reshape(- 1 ,1 ), 3 , axis=- 1 )print ('input shape:' , t.shape)= SlidingWindow(wl, stride= stride, pad_remainder= True , get_y= [])(t)= tensor(X)0 , 1 , - 2 :] = np.nan1 ,..., :3 ] = np.nanprint (X)float ())
input shape: (13, 3)
tensor([[[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4.],
[ 0., 1., 2., nan, nan],
[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]],
[[nan, nan, nan, 8., 9.],
[nan, nan, nan, 8., 9.],
[nan, nan, nan, 8., 9.],
[nan, nan, nan, 0., 0.]],
[[10., 11., 12., nan, nan],
[10., 11., 12., nan, nan],
[10., 11., 12., nan, nan],
[ 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.]]])
tensor([[[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]],
[[1., 1., 1., 0., 0.],
[1., 1., 1., 0., 0.],
[1., 1., 1., 0., 0.],
[1., 1., 1., 0., 0.]],
[[0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]]])
Forecasting data preparation
source
basic_data_preparation_fn
basic_data_preparation_fn (df, drop_duplicates=True, datetime_col=None,
use_index=False, keep='last',
add_missing_datetimes=True, freq='1D',
method=None, sort_by=None)
df
dataframe to preprocess
drop_duplicates
bool
True
flag to indicate if rows with duplicate datetime info should be removed
datetime_col
NoneType
None
str indicating the name of the column/s that contains the datetime info
use_index
bool
False
flag to indicate if the datetime info is in the index
keep
str
last
str to indicate what data should be kept in case of duplicate rows
add_missing_datetimes
bool
True
flaf to indicate if missing datetimes should be added
freq
str
1D
str to indicate the frequency used in the datetime info. Used in case missing timestamps exists
method
NoneType
None
str indicating the method used to fill data for missing timestamps: None, ‘bfill’, ‘ffill’
sort_by
NoneType
None
str or list of str to indicate if how to sort data. If use_index=True the index will be used to sort the dataframe.
= 100 = 'datetime' = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(df_len), columns= ['value' ])'datetime' ] = pd.date_range(pd.to_datetime('1749-03-31' ), periods= df_len, freq= '1D' )'type' ] = 1 # drop 10 rows at random = df.drop(df.sample(10 ).index)# add 2 duplicated rows = pd.concat([df, df.sample(2 )])= basic_data_preparation_fn(df, drop_duplicates= True , datetime_col= datetime_col, use_index= False , keep= 'last' , = True , freq= '1D' , method= 'ffill' , sort_by= datetime_col)
0
0
1749-03-31
1
1
1
1749-04-01
1
3
3
1749-04-03
1
4
4
1749-04-04
1
5
5
1749-04-05
1
...
...
...
...
96
96
1749-07-05
1
97
97
1749-07-06
1
99
99
1749-07-08
1
0
0
1749-03-31
1
19
19
1749-04-19
1
92 rows × 3 columns
0
0
1749-03-31
1
1
1
1749-04-01
1
2
1
1749-04-02
1
3
3
1749-04-03
1
4
4
1749-04-04
1
...
...
...
...
95
95
1749-07-04
1
96
96
1749-07-05
1
97
97
1749-07-06
1
98
97
1749-07-07
1
99
99
1749-07-08
1
100 rows × 3 columns
source
check_safe_conversion
check_safe_conversion (o, dtype='float32', cols=None)
Checks if the conversion to float is safe
assert check_safe_conversion(- 2 ** 11 , 'float16' ) == True assert check_safe_conversion(- 2 ** 11 - 1 , 'float16' ) == False assert check_safe_conversion(2 ** 24 , 'float32' ) == True assert check_safe_conversion(2 ** 24 + 1 , 'float32' ) == False assert check_safe_conversion(2 ** 53 , 'float64' ) == True assert check_safe_conversion(2 ** 53 + 1 , 'float64' ) == False = pd.DataFrame({'a' : [1 , 2 , 3 ], 'b' : [2 ** 24 , 2 ** 24 + 1 , 2 ** 24 + 2 ]})assert not check_safe_conversion(df, 'float32' )assert check_safe_conversion(df, 'int32' )assert check_safe_conversion(df, 'float32' , cols= 'a' )assert not check_safe_conversion(df, 'float32' , cols= 'b' )
-2147483648 1 3 2147483647
-2147483648 16777216 16777218 2147483647
/var/folders/42/4hhwknbd5kzcbq48tmy_gbp00000gn/T/ipykernel_30986/657350933.py:39: UserWarning: Unsafe conversion to float32: {'a': True, 'b': False}
warnings.warn(f"Unsafe conversion to {dtype}: {dict(zip(cols, checks))}")
/var/folders/42/4hhwknbd5kzcbq48tmy_gbp00000gn/T/ipykernel_30986/657350933.py:39: UserWarning: Unsafe conversion to float32: {'b': False}
warnings.warn(f"Unsafe conversion to {dtype}: {dict(zip(cols, checks))}")
source
prepare_forecasting_data
from tsai.data.validation import get_forecasting_splits
= 10 = 5 = 1 = 0.2 = 0.2 = pd.DataFrame()'target' ] = np.arange(50 )= prepare_forecasting_data(df, fcst_history, fcst_horizon)= get_forecasting_splits(df, fcst_history, fcst_horizon, valid_size= valid_size, test_size= test_size, stride= stride, show_plot= False )assert y[splits[0 ]][- 1 ][0 ][- 1 ] == y[splits[1 ]][0 ][0 ][0 ] - strideassert y[splits[1 ]][- 1 ][0 ][- 1 ] == y[splits[2 ]][0 ][0 ][0 ] - stridefor s,t in zip (splits, [' \n train_split:' , ' \n valid_split:' , ' \n test_split :' ]):print (t)for xi, yi in zip (X[s], y[s]):print (xi, yi)
train_split:
[[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]] [[10 11 12 13 14]]
[[ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10]] [[11 12 13 14 15]]
[[ 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11]] [[12 13 14 15 16]]
[[ 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12]] [[13 14 15 16 17]]
[[ 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13]] [[14 15 16 17 18]]
[[ 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14]] [[15 16 17 18 19]]
[[ 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15]] [[16 17 18 19 20]]
[[ 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16]] [[17 18 19 20 21]]
[[ 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17]] [[18 19 20 21 22]]
[[ 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18]] [[19 20 21 22 23]]
[[10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19]] [[20 21 22 23 24]]
[[11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20]] [[21 22 23 24 25]]
[[12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21]] [[22 23 24 25 26]]
[[13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22]] [[23 24 25 26 27]]
[[14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23]] [[24 25 26 27 28]]
[[15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24]] [[25 26 27 28 29]]
valid_split:
[[20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29]] [[30 31 32 33 34]]
[[21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30]] [[31 32 33 34 35]]
[[22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31]] [[32 33 34 35 36]]
[[23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32]] [[33 34 35 36 37]]
[[24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33]] [[34 35 36 37 38]]
[[25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34]] [[35 36 37 38 39]]
test_split :
[[30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39]] [[40 41 42 43 44]]
[[31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40]] [[41 42 43 44 45]]
[[32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41]] [[42 43 44 45 46]]
[[33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42]] [[43 44 45 46 47]]
[[34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43]] [[44 45 46 47 48]]
[[35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44]] [[45 46 47 48 49]]
= 10 = 5 = 1 = 0.2 = 0.2 = pd.DataFrame()'target' ] = np.arange(50 )= prepare_forecasting_data(df, fcst_history, fcst_horizon, x_vars= None , y_vars= [])= get_forecasting_splits(df, fcst_history, fcst_horizon, valid_size= valid_size, test_size= test_size, stride= stride, show_plot= False )assert y is None
= 100 = 3 = 'datetime' = pd.DataFrame()for i in range (n_values):f"value_ { i} " ] = (np.arange(df_len) * 10 ** i).astype(np.float32)= 10 = 5 = df.columns= None = None = prepare_forecasting_data(df, fcst_history= fcst_history, fcst_horizon= fcst_horizon, x_vars= x_vars, y_vars= y_vars, dtype= dtype)86 , 3 , 10 ))86 , 3 , 5 ))3 , :, 0 ], X[:3 , :, - 1 ] + np.array([1 , 10 , 100 ]).reshape(1 , 1 , - 1 ))print (X[:3 ].astype(int ))print (y[:3 ].astype(int ))
0
0.0
0.0
0.0
1
1.0
10.0
100.0
2
2.0
20.0
200.0
3
3.0
30.0
300.0
4
4.0
40.0
400.0
...
...
...
...
95
95.0
950.0
9500.0
96
96.0
960.0
9600.0
97
97.0
970.0
9700.0
98
98.0
980.0
9800.0
99
99.0
990.0
9900.0
100 rows × 3 columns
[[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
[ 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90]
[ 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900]]
[[ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10]
[ 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100]
[ 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000]]
[[ 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11]
[ 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110]
[ 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100]]]
[[[ 10 11 12 13 14]
[ 100 110 120 130 140]
[1000 1100 1200 1300 1400]]
[[ 11 12 13 14 15]
[ 110 120 130 140 150]
[1100 1200 1300 1400 1500]]
[[ 12 13 14 15 16]
[ 120 130 140 150 160]
[1200 1300 1400 1500 1600]]]
= 100 = 3 = 'datetime' = pd.DataFrame()for i in range (n_values):f"value_ { i} " ] = (np.arange(df_len) * 10 ** (i + 1 )).astype(np.float32)'datetime' ] = pd.date_range(pd.to_datetime('1749-03-31' ), periods= df_len, freq= '1D' )'type' ] = np.random.randint(0 , 4 , df_len)'target' ] = np.arange(df_len)= 10 = 5 = ['value_0' , 'value_1' , 'value_2' , 'target' ]= 'target' = np.float32= prepare_forecasting_data(df, fcst_history= fcst_history, fcst_horizon= fcst_horizon, x_vars= x_vars, y_vars= y_vars, dtype= dtype)86 , 4 , 10 ))86 , 1 , 5 ))print (X[:3 ].astype(int ))print (y[:3 ])
0
0.0
0.0
0.0
1749-03-31
3
0
1
10.0
100.0
1000.0
1749-04-01
1
1
2
20.0
200.0
2000.0
1749-04-02
1
2
3
30.0
300.0
3000.0
1749-04-03
1
3
4
40.0
400.0
4000.0
1749-04-04
2
4
...
...
...
...
...
...
...
95
950.0
9500.0
95000.0
1749-07-04
0
95
96
960.0
9600.0
96000.0
1749-07-05
0
96
97
970.0
9700.0
97000.0
1749-07-06
3
97
98
980.0
9800.0
98000.0
1749-07-07
2
98
99
990.0
9900.0
99000.0
1749-07-08
1
99
100 rows × 6 columns
[[[ 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90]
[ 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900]
[ 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000]
[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]]
[[ 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100]
[ 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000]
[ 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000]
[ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10]]
[[ 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110]
[ 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100]
[ 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000 11000]
[ 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11]]]
[[[10. 11. 12. 13. 14.]]
[[11. 12. 13. 14. 15.]]
[[12. 13. 14. 15. 16.]]]
source
get_today
get_today (datetime_format='%Y-%m-%d')
"%Y-%m- %d " ))
source
split_fcst_datetime
split_fcst_datetime (fcst_datetime)
Define fcst start and end dates
fcst_datetime
str or list of str with datetime
None ), (None , None ))'2020-01-01' ), ('2020-01-01' , '2020-01-01' ))'2019-01-01' , '2020-01-01' ]), ['2019-01-01' , '2020-01-01' ])
source
set_df_datetime
set_df_datetime (df, datetime_col=None, use_index=False)
Make sure datetime column or index is of the right date type.
# Test = 100 = 3 = 'datetime' = pd.DataFrame()for i in range (n_values):f"value_ { i} " ] = (np.arange(df_len) * 10 ** (i + 1 )).astype(np.float32)'datetime' ] = pd.date_range(pd.to_datetime('1749-03-31' ), periods= df_len, freq= '1D' )= datetime_col)'datetime' ].dtypes, np.dtype('datetime64[ns]' ))= df.set_index('datetime' )= True )'datetime64[ns]' ))
source
get_df_datetime_bounds
get_df_datetime_bounds (df, datetime_col=None, use_index=False)
Returns the start date and and dates used by the forecast
df
dataframe containing forecasting data
datetime_col
NoneType
None
str data column containing the datetime
use_index
bool
False
bool flag to indicate if index should be used to get column
# Test = 100 = 3 = 'datetime' = pd.DataFrame()for i in range (n_values):f"value_ { i} " ] = (np.arange(df_len) * 10 ** (i + 1 )).astype(np.float32)'datetime' ] = pd.date_range(pd.to_datetime('1749-03-31' ), periods= df_len, freq= '1D' )= datetime_col), (df['datetime' ].min (), df['datetime' ].max ()))= df.set_index('datetime' )= True ), (df_index.index.min (), df_index.index.max ()))
source
get_fcst_bounds
get_fcst_bounds (df, fcst_datetime, fcst_history=None, fcst_horizon=None,
freq='D', datetime_format='%Y-%m-%d', datetime_col=None,
use_index=False)
Returns the start and end datetimes used by the forecast
df
dataframe containing forecasting data
fcst_datetime
datetime for which a fcst is created. Optionally tuple of datatimes if the fcst is created for a range of dates.
fcst_history
NoneType
None
# steps used as input
fcst_horizon
NoneType
None
# predicted steps
freq
str
D
datetime units. May contain a letters only or a combination of ints + letters: eg. “7D”
datetime_format
str
%Y-%m-%d
format used to convert “today”
datetime_col
NoneType
None
str data column containing the datetime
use_index
bool
False
bool flag to indicate if index should be used to get column
from datetime import timedelta
# Test = 100 = 3 = 'datetime' = pd.DataFrame()for i in range (n_values):f"value_ { i} " ] = (np.arange(df_len) * 10 ** (i + 1 )).astype(np.float32)= "7D" = pd.Timestamp(get_today()).floor(freq)'datetime' ] = pd.date_range(None , today, periods= df_len, freq= freq)= pd.Timestamp(df['datetime' ].max ()).floor(freq)= 30 = 10 = max_dt - timedelta(weeks= fcst_horizon)print ('fcst_datetime :' , fcst_datetime)= get_fcst_bounds(df, fcst_datetime, datetime_col= datetime_col, fcst_history= fcst_history, fcst_horizon= fcst_horizon, freq= freq)print ('start_datetime:' , start_datetime)print ('end_datetime :' , end_datetime)= pd.date_range(start_datetime, end_datetime, freq= freq)print (dates)len (dates), fcst_history + fcst_horizon)
0
0.0
0.0
0.0
2021-11-25
1
10.0
100.0
1000.0
2021-12-02
2
20.0
200.0
2000.0
2021-12-09
3
30.0
300.0
3000.0
2021-12-16
4
40.0
400.0
4000.0
2021-12-23
...
...
...
...
...
95
950.0
9500.0
95000.0
2023-09-21
96
960.0
9600.0
96000.0
2023-09-28
97
970.0
9700.0
97000.0
2023-10-05
98
980.0
9800.0
98000.0
2023-10-12
99
990.0
9900.0
99000.0
2023-10-19
100 rows × 4 columns
fcst_datetime : 2023-08-10 00:00:00
start_datetime: 2023-01-19 00:00:00
end_datetime : 2023-10-19 00:00:00
DatetimeIndex(['2023-01-19', '2023-01-26', '2023-02-02', '2023-02-09',
'2023-02-16', '2023-02-23', '2023-03-02', '2023-03-09',
'2023-03-16', '2023-03-23', '2023-03-30', '2023-04-06',
'2023-04-13', '2023-04-20', '2023-04-27', '2023-05-04',
'2023-05-11', '2023-05-18', '2023-05-25', '2023-06-01',
'2023-06-08', '2023-06-15', '2023-06-22', '2023-06-29',
'2023-07-06', '2023-07-13', '2023-07-20', '2023-07-27',
'2023-08-03', '2023-08-10', '2023-08-17', '2023-08-24',
'2023-08-31', '2023-09-07', '2023-09-14', '2023-09-21',
'2023-09-28', '2023-10-05', '2023-10-12', '2023-10-19'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='7D')
source
filter_df_by_datetime
filter_df_by_datetime (df, start_datetime=None, end_datetime=None,
datetime_col=None, use_index=False)
df
dataframe containing forecasting data
start_datetime
NoneType
None
lower datetime bound
end_datetime
NoneType
None
upper datetime bound
datetime_col
NoneType
None
str data column containing the datetime
use_index
bool
False
bool flag to indicate if index should be used to get column
# Test = 100 = 3 = 'datetime' = pd.DataFrame()for i in range (n_values):f"value_ { i} " ] = (np.arange(df_len) * 10 ** (i + 1 )).astype(np.float32)= "7D" 'datetime' ] = pd.date_range(None , pd.Timestamp(get_today()).floor(freq), periods= df_len, freq= freq)= pd.Timestamp(df['datetime' ].max ()).floor(freq)= 30 = 10 = pd.date_range(end= fcst_datetime, periods= fcst_horizon + 1 , freq= freq).floor(freq)[- 1 ]= get_fcst_bounds(df, fcst_datetime, datetime_col= datetime_col, fcst_history= fcst_history, fcst_horizon= fcst_horizon, freq= freq)len (filter_df_by_datetime(df, start_datetime= start_datetime, end_datetime= end_datetime, datetime_col= datetime_col)), fcst_history + fcst_horizon)
0
0.0
0.0
0.0
2021-11-25
1
10.0
100.0
1000.0
2021-12-02
2
20.0
200.0
2000.0
2021-12-09
3
30.0
300.0
3000.0
2021-12-16
4
40.0
400.0
4000.0
2021-12-23
...
...
...
...
...
95
950.0
9500.0
95000.0
2023-09-21
96
960.0
9600.0
96000.0
2023-09-28
97
970.0
9700.0
97000.0
2023-10-05
98
980.0
9800.0
98000.0
2023-10-12
99
990.0
9900.0
99000.0
2023-10-19
100 rows × 4 columns
source
get_fcst_data_from_df
get_fcst_data_from_df (df, fcst_datetime, fcst_history=None,
fcst_horizon=None, freq='D',
datetime_format='%Y-%m-%d', datetime_col=None,
use_index=False)
Get forecasting data from a dataframe
df
dataframe containing forecasting data
fcst_datetime
datetime for which a fcst is created. Optionally tuple of datatimes if the fcst is created for a range of dates.
fcst_history
NoneType
None
# steps used as input
fcst_horizon
NoneType
None
# predicted steps
freq
str
D
datetime units. May contain a letters only or a combination of ints + letters: eg. “7D”
datetime_format
str
%Y-%m-%d
format used to convert “today”
datetime_col
NoneType
None
str data column containing the datetime
use_index
bool
False
bool flag to indicate if index should be used to get column
# Test = 100 = 3 = 'datetime' = pd.DataFrame()for i in range (n_values):f"value_ { i} " ] = (np.arange(df_len) * 10 ** (i + 1 )).astype(np.float32)= "7D" 'datetime' ] = pd.date_range(None , pd.Timestamp(get_today()).floor(freq), periods= df_len, freq= freq)= pd.Timestamp(df['datetime' ].max ()).floor(freq)= 30 = 10 = pd.date_range(end= fcst_datetime, periods= fcst_horizon + 1 , freq= freq).floor(freq)[- 1 ]len (get_fcst_data_from_df(df, fcst_datetime, fcst_history= fcst_history, fcst_horizon= fcst_horizon, freq= freq, datetime_col= datetime_col)), + fcst_horizon)
0
0.0
0.0
0.0
2021-11-25
1
10.0
100.0
1000.0
2021-12-02
2
20.0
200.0
2000.0
2021-12-09
3
30.0
300.0
3000.0
2021-12-16
4
40.0
400.0
4000.0
2021-12-23
...
...
...
...
...
95
950.0
9500.0
95000.0
2023-09-21
96
960.0
9600.0
96000.0
2023-09-28
97
970.0
9700.0
97000.0
2023-10-05
98
980.0
9800.0
98000.0
2023-10-12
99
990.0
9900.0
99000.0
2023-10-19
100 rows × 4 columns