General helper functions used throughout the library
source
random_rand
random_rand (*d, dtype=None, out=None, seed=None)
Same as np.random.rand but with a faster random generator, dtype and seed
d
VAR_POSITIONAL
int or tuple of ints, optional. The dimensions of the returned array, must be non-negative.
dtype
NoneType
None
data type of the output.
out
NoneType
None
ndarray, optional. Alternative output array in which to place the result.
seed
NoneType
None
int or None, optional. Seed for the random number generator.
source
random_randint
random_randint (low, high=None, size=None, dtype=<class 'int'>,
endpoint=False, seed=None)
Same as np.random.randint but with a faster random generator and seed
low
int, lower endpoint of interval (inclusive)
high
NoneType
None
int, upper endpoint of interval (exclusive), or None for a single-argument form of low.
size
NoneType
None
int or tuple of ints, optional. Output shape.
dtype
type
int
data type of the output.
endpoint
bool
False
bool, optional. If True, high is an inclusive endpoint. If False, the range is open on the right.
seed
NoneType
None
int or None, optional. Seed for the random number generator.
source
random_choice
random_choice (a, size=None, replace=True, p=None, axis=0, shuffle=True,
dtype=None, seed=None)
Same as np.random.choice but with a faster random generator, dtype and seed
a
1-D array-like or int. The values from which to draw the samples.
size
NoneType
None
int or tuple of ints, optional. The shape of the output.
replace
bool
True
bool, optional. Whether or not to allow the same value to be drawn multiple times.
p
NoneType
None
1-D array-like, optional. The probabilities associated with each entry in a.
axis
int
0
int, optional. The axis along which the samples are drawn.
shuffle
bool
True
bool, optional. Whether or not to shuffle the samples before returning them.
dtype
NoneType
None
data type of the output.
seed
NoneType
None
int or None, optional. Seed for the random number generator.
= random_choice(10 , size= (2 ,3 ,4 ), replace= True , p= None , seed= 1 )= random_choice(10 , size= (2 ,3 ,4 ), replace= True , p= None , seed= 1 )= random_choice(10 , size= (2 ,3 ,4 ), replace= True , p= None , seed= 2 )assert random_choice(10 , size= 3 , replace= True , p= None ).shape == (3 ,)assert random_choice(10 , size= (2 ,3 ,4 ), replace= True , p= None ).shape == (2 ,3 ,4 )print (random_choice(10 , size= 3 , replace= True , p= None ))print (random_choice(10 , size= 3 , replace= False , p= None ))= [2 , 5 , 4 , 9 , 13 , 25 , 56 , 83 , 99 , 100 ]print (random_choice(a, size= 3 , replace= False , p= None ))
[5 7 5]
[0 1 6]
[ 4 83 100]
= random_randint(10 , 20 , 100 , seed= 1 )= random_randint(10 , 20 , 100 , seed= 1 )= random_randint(10 , 20 , 100 , seed= 2 )assert (a >= 10 ).all () and (a < 20 ).all ()
= random_rand(2 , 3 , 4 , seed= 123 )= random_rand(2 , 3 , 4 , seed= 123 )= random_rand(2 , 3 , 4 , seed= 124 )assert (a >= 0 ).all () and (a < 1 ).all ()= random_rand(2 , 3 , 4 )= a.copy()2 , 3 , 4 , out= a)
source
is_memmap
is_memmap (o)
source
is_tensor
is_tensor (o)
source
is_nparray
is_nparray (o)
# ensure these folders exist for testing purposes = ['data' , 'export' , 'models' ]for fn in fns:= Path('.' )/ fnif not os.path.exists(path): os.makedirs(path)
source
todtype
todtype (dtype)
source
to3dPlusArray
to3dPlusArray (o)
source
to3dPlusTensor
to3dPlusTensor (o)
source
to2dPlusArray
to2dPlusArray (o)
source
to2dPlusTensor
to2dPlusTensor (o)
source
to1darray
to1darray (o)
source
to2darray
to2darray (o)
source
to3darray
to3darray (o)
source
to1dtensor
to1dtensor (o)
source
to2dtensor
to2dtensor (o)
source
to3dtensor
to3dtensor (o)
source
totensor
totensor (o)
= np.random.rand(100 ).astype(np.float32)= torch.from_numpy(a).float ()3 )2 )1 )3 )2 )1 )
= np.random.rand(10 , 20 )= pd.DataFrame(data)'target' ] = np.random.randint(0 , 3 , len (df))= df[df.columns[:- 1 ]]= df['target' ]10 , 1 , 20 ))10 ,))
source
get_file_size
get_file_size (file_path:str, return_str:bool=True, decimals:int=2)
file_path
str
path to file
return_str
bool
True
True returns size in human-readable format (KB, MB, GB, …). False in bytes.
decimals
int
2
Number of decimals in the output
source
get_dir_size
get_dir_size (dir_path:str, return_str:bool=True, decimals:int=2,
verbose:bool=False)
dir_path
str
path to directory
return_str
bool
True
True returns size in human-readable format (KB, MB, GB, …). False in bytes.
decimals
int
2
Number of decimals in the output
verbose
bool
False
Controls verbosity
source
get_size
get_size (o, return_str=False, decimals=2)
o
Any python object
return_str
bool
False
True returns size in human-readable format (KB, MB, GB, …). False in bytes.
decimals
int
2
Number of decimals in the output
source
bytes2str
bytes2str (size_bytes:int, decimals=2)
size_bytes
int
Number of bytes
decimals
int
2
Number of decimals in the output
Returns str
= np.random.rand(10 , 5 , 3 )True , 1 ), '1.2 KB' )
source
is_np_view
is_np_view (o)
= np.array([1. , 2. , 3. ])False )1 :]), True )
source
is_file
is_file (path)
"002_utils.ipynb" ), True )"utils.ipynb" ), False )
source
delete_all_in_dir
delete_all_in_dir (tgt_dir, exception=None)
source
reverse_dict
reverse_dict (dictionary)
source
itemify
itemify (*o, tup_id=None)
= [1 , 2 , 3 ]= [4 , 5 , 6 ]print (itemify(a, b))len (itemify(a, b)), len (a))= [1 , 2 , 3 ]= None print (itemify(a, b))len (itemify(a, b)), len (a))= [1 , 2 , 3 ]= [4 , 5 , 6 ]= None print (itemify(a, b, c))len (itemify(a, b, c)), len (a))
[(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)]
[(1,), (2,), (3,)]
[(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)]
source
ifelse
ifelse (a, b, c)
b if a is True else c
source
isnone
isnone (o)
= np.array(3 )False )True )= None True )False )
source
test_eq_nan
test_eq_nan (a, b)
test that a==b excluding nan values (valid for torch.Tensor and np.ndarray)
source
test_error
test_error (error, f, *args, **kwargs)
source
test_not_ok
test_not_ok (f, *args, **kwargs)
source
test_ok
test_ok (f, *args, **kwargs)
source
test_type
test_type (a, b)
source
test_not_close
test_not_close (a, b, eps=1e-05)
test that a is within eps of b
source
is_not_close
is_not_close (a, b, eps=1e-05)
Is a within eps of b
source
assert_fn
assert_fn (*args, **kwargs)
source
test_le
test_le (a, b)
test that a>b
source
test_lt
test_lt (a, b)
test that a>b
source
test_ge
test_ge (a, b)
test that a>=b
source
test_gt
test_gt (a, b)
test that a>b
5 , 4 )4 , 4 )4 , 4 )3 , 4 )3 , 4 )4 , 4 )4 , 4 )5 , 4 )
= torch.rand(100 )
source
stack_pad
stack_pad (o, padding_value=nan)
Converts a an iterable into a numpy array using padding if necessary
source
stack
stack (o, axis=0, retain=True)
= [[0 ,1 ,2 ], [4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ]]1 , 2 , 4 ))type (stack_pad(o)), np.ndarray)sum (), 1 )
= 3 print (stack_pad(o))3. ]]))= [4 ,5 ]print (stack_pad(o))4. , 5. ]]))= [[0 ,1 ,2 ], [4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ]]print (stack_pad(o))= np.array([0 , [1 ,2 ]], dtype= object )print (stack_pad(o))= np.array([[[0 ], [10 , 20 ], [100 , 200 , 300 ]], [[0 , 1 , 2 , 3 ], [10 , 20 ], [100 ]]], dtype= object )print (stack_pad(o))= np.array([0 , [10 , 20 ]], dtype= object )print (stack_pad(o))
[[3.]]
[[4. 5.]]
[[[ 0. 1. 2. nan]
[ 4. 5. 6. 7.]]]
[[ 0. nan]
[ 1. 2.]]
[[[ 0. nan nan nan]
[ 10. 20. nan nan]
[100. 200. 300. nan]]
[[ 0. 1. 2. 3.]
[ 10. 20. nan nan]
[100. nan nan nan]]]
[[ 0. nan]
[10. 20.]]
= np.random.rand(2 , 3 , 4 )= torch.from_numpy(a)= 0 )), a)= 0 )), t)
source
pad_sequences
pad_sequences (o, maxlen:int=None,
dtype:(<class'str'>,<class'type'>)=<class
'numpy.float64'>, padding:str='pre', truncating:str='pre',
padding_value:float=nan)
Transforms an iterable with sequences into a 3d numpy array using padding or truncating sequences if necessary
o
Iterable object
maxlen
int
None
Optional max length of the output. If None, max length of the longest individual sequence.
dtype
(<class ‘str’>, <class ‘type’>)
float64
Type of the output sequences. To pad sequences with variable length strings, you can use object.
padding
str
pre
‘pre’ or ‘post’ pad either before or after each sequence.
truncating
str
pre
‘pre’ or ‘post’ remove values from sequences larger than maxlen, either at the beginning or at the end of the sequences.
padding_value
float
nan
Value used for padding.
This function transforms a list (of length n_samples) of sequences into a 3d numpy array of shape:
[n_samples x n_vars x seq_len]seq_len is either the maxlen argument if provided, or the length of the longest sequence in the list.
Sequences that are shorter than seq_len are padded with value until they are seq_len long.
Sequences longer than seq_len are truncated so that they fit the desired length.
The position where padding or truncation happens is determined by the arguments padding and truncating, respectively. Pre-padding or removing values from the beginning of the sequence is the default.
Input sequences to pad_sequences may be have 1, 2 or 3 dimensions:
# 1 dim = np.arange(6 )= np.arange(3 ) * 10 = np.arange(2 ) * 100 = [a1, a2, a3]= pad_sequences(o, maxlen= 4 , dtype= np.float64, padding= 'post' , truncating= 'pre' , padding_value= np.nan)3 , 1 , 4 ))
array([[[ 2., 3., 4., 5.]],
[[ 0., 10., 20., nan]],
[[ 0., 100., nan, nan]]])
# 2 dim = np.arange(12 ).reshape(2 , 6 )= np.arange(6 ).reshape(2 , 3 ) * 10 = np.arange(4 ).reshape(2 , 2 ) * 100 = [a1, a2, a3]= pad_sequences(o, maxlen= 4 , dtype= np.float64, padding= 'post' , truncating= 'pre' , padding_value= np.nan)3 , 2 , 4 ))
array([[[ 2., 3., 4., 5.],
[ 8., 9., 10., 11.]],
[[ 0., 10., 20., nan],
[ 30., 40., 50., nan]],
[[ 0., 100., nan, nan],
[200., 300., nan, nan]]])
# 3 dim = np.arange(10 ).reshape(1 , 2 , 5 )= np.arange(6 ).reshape(1 , 2 , 3 ) * 10 = np.arange(4 ).reshape(1 , 2 , 2 ) * 100 = [a1, a2, a3]= pad_sequences(o, maxlen= None , dtype= np.float64, padding= 'pre' , truncating= 'pre' , padding_value= np.nan)3 , 2 , 5 ))
array([[[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4.],
[ 5., 6., 7., 8., 9.]],
[[ nan, nan, 0., 10., 20.],
[ nan, nan, 30., 40., 50.]],
[[ nan, nan, nan, 0., 100.],
[ nan, nan, nan, 200., 300.]]])
# 3 dim = np.arange(10 ).reshape(1 , 2 , 5 )= np.arange(6 ).reshape(1 , 2 , 3 ) * 10 = np.arange(4 ).reshape(1 , 2 , 2 ) * 100 = [a1, a2, a3]= pad_sequences(o, maxlen= 4 , dtype= np.float64, padding= 'pre' , truncating= 'pre' , padding_value= np.nan)3 , 2 , 4 ))
array([[[ 1., 2., 3., 4.],
[ 6., 7., 8., 9.]],
[[ nan, 0., 10., 20.],
[ nan, 30., 40., 50.]],
[[ nan, nan, 0., 100.],
[ nan, nan, 200., 300.]]])
# 3 dim = np.arange(10 ).reshape(1 , 2 , 5 )= np.arange(6 ).reshape(1 , 2 , 3 ) * 10 = np.arange(4 ).reshape(1 , 2 , 2 ) * 100 = [a1, a2, a3]= pad_sequences(o, maxlen= 4 , dtype= np.float64, padding= 'post' , truncating= 'pre' , padding_value= np.nan)3 , 2 , 4 ))
array([[[ 1., 2., 3., 4.],
[ 6., 7., 8., 9.]],
[[ 0., 10., 20., nan],
[ 30., 40., 50., nan]],
[[ 0., 100., nan, nan],
[200., 300., nan, nan]]])
# 3 dim = np.arange(10 ).reshape(1 , 2 , 5 )= np.arange(6 ).reshape(1 , 2 , 3 ) * 10 = np.arange(4 ).reshape(1 , 2 , 2 ) * 100 = [a1, a2, a3]= pad_sequences(o, maxlen= 4 , dtype= np.float64, padding= 'post' , truncating= 'post' , padding_value= np.nan)3 , 2 , 4 ))
array([[[ 0., 1., 2., 3.],
[ 5., 6., 7., 8.]],
[[ 0., 10., 20., nan],
[ 30., 40., 50., nan]],
[[ 0., 100., nan, nan],
[200., 300., nan, nan]]])
# iterable is a list of lists = np.arange(12 ).reshape(1 , 2 , 6 ).tolist()= (np.arange(6 ).reshape(1 , 2 , 3 ) * 10 ).tolist()= (np.arange(4 ).reshape(1 , 2 , 2 ) * 100 ).tolist()= [a1, a2, a3]= pad_sequences(o, maxlen= None , dtype= np.float64, padding= 'post' , truncating= 'pre' , padding_value= np.nan)3 , 2 , 6 ))
array([[[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5.],
[ 6., 7., 8., 9., 10., 11.]],
[[ 0., 10., 20., nan, nan, nan],
[ 30., 40., 50., nan, nan, nan]],
[[ 0., 100., nan, nan, nan, nan],
[200., 300., nan, nan, nan, nan]]])
source
match_seq_len
match_seq_len (*arrays)
= np.random.rand(10 , 5 , 8 )= np.random.rand(3 , 5 , 10 )= match_seq_len(a, b)- 1 ], d.shape[- 1 ])
source
random_shuffle
random_shuffle (o, random_state=None)
= np.arange(10 )1 ), np.array([2 , 9 , 6 , 4 , 0 , 3 , 1 , 7 , 8 , 5 ]))= torch.arange(10 )1 ), tensor([2 , 9 , 6 , 4 , 0 , 3 , 1 , 7 , 8 , 5 ]))= list (a)1 ), [2 , 9 , 6 , 4 , 0 , 3 , 1 , 7 , 8 , 5 ])= L(l)1 ), L([2 , 9 , 6 , 4 , 0 , 3 , 1 , 7 , 8 , 5 ]))
source
cat2int
cat2int (o)
= np.array(['b' , 'a' , 'a' , 'b' , 'a' , 'b' , 'a' ])1 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 ]))
source
cycle_dl_estimate
cycle_dl_estimate (dl, iters=10)
source
cycle_dl_to_device
cycle_dl_to_device (dl, show_progress_bar=True)
source
cycle_dl
cycle_dl (dl, show_progress_bar=True)
source
cache_data
cache_data (o, slice_len=10000, verbose=False)
source
get_func_defaults
get_func_defaults (f)
source
get_idx_from_df_col_vals
get_idx_from_df_col_vals (df, col, val_list)
source
get_sublist_idxs
get_sublist_idxs (aList, bList)
Get idxs that when applied to aList will return bList. aList must contain all values in bList
= np.array([3 , 5 , 7 , 1 , 9 , 8 , 6 , 2 ])= np.array([6 , 1 , 5 , 7 ])= get_sublist_idxs(x, y)= np.array([3 , 5 , 7 , 1 , 9 , 8 , 6 , 6 , 2 ])= np.array([6 , 1 , 5 , 7 , 5 ])= get_sublist_idxs(x, y)
source
flatten_list
flatten_list (l)
source
display_pd_df
display_pd_df (df, max_rows:Union[bool,int]=False,
max_columns:Union[bool,int]=False)
= pd.get_option('display.max_rows' ), pd.get_option('display.max_columns' )= pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(70 , 25 ))= 2 , max_columns= 3 )'display.max_rows' ))'display.max_columns' ))
0
0.436034
...
0.231616
...
...
...
...
69
0.633051
...
0.051762
70 rows × 25 columns
source
kstest
kstest (data1, data2, alternative='two-sided', mode='auto', by_axis=None)
*Performs the two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for goodness of fit.
Parameters data1, data2: Two arrays of sample observations assumed to be drawn from a continuous distributions. Sample sizes can be different. alternative: {‘two-sided’, ‘less’, ‘greater’}, optional. Defines the null and alternative hypotheses. Default is ‘two-sided’. mode: {‘auto’, ‘exact’, ‘asymp’}, optional. Defines the method used for calculating the p-value. by_axis (optional, int): for arrays with more than 1 dimension, the test will be run for each variable in that axis if by_axis is not None.*
source
ttest
ttest (data1, data2, equal_var=False)
Calculates t-statistic and p-value based on 2 sample distributions
= np.random.normal(0.5 , 1 , 100 )= np.random.normal(0.15 , .5 , 50 )50 )50 )
= np.random.normal(0.5 , 1 , (100 ,3 ))= np.random.normal(0.5 , 1 , (50 ,))
(0.22333333333333333, 0.02452803315700394)
= np.random.normal(0.5 , 1 , (100 ,3 ))= np.random.normal(0.15 , .5 , (50 ,))
(0.31, 0.0004061333917852463)
= np.random.normal(0 ,1 ,(100 , 5 , 3 ))= np.random.normal(0 ,2 ,(100 , 5 , 3 ))= 1 )
([0.22,
0.16333333333333333,
0.16333333333333333,
0.18666666666666668,
0.21666666666666667],
[8.994053173844458e-07,
0.0006538374533623971,
0.0006538374533623971,
5.522790313356146e-05,
1.4007759411179028e-06])
= np.random.normal(0.5 , 1 , 100 )= torch.normal(0.5 , 1 , (100 , ))
(4.33309224863388, tensor(5.7798))
source
remove_fn
remove_fn (fn, verbose=False)
Removes a file (fn) if exists
source
npsave
npsave (array_fn, array, verbose=True)
= 'data/remove_fn_test.npy' = np.zeros(1 )del a= 'r+' )True )True )
data/remove_fn_test.npy does not exist
saving data/remove_fn_test.npy...
...data/remove_fn_test.npy saved
data/remove_fn_test.npy file removed
data/remove_fn_test.npy does not exist
source
permute_2D
permute_2D (array, axis=None)
Permute rows or columns in an array. This can be used, for example, in feature permutation
= np.arange(100 * 50 ).reshape(100 , 50 )= 0 ).mean(0 ), s.mean(0 ))= 0 ), s)= 1 ).mean(1 ), s.mean(1 ))= 1 ), s)
source
random_half_normal_tensor
random_half_normal_tensor (shape=1, device=None)
Returns a tensor of a predefined shape between 0 and 1 with a half-normal distribution
source
random_normal_tensor
random_normal_tensor (shape=1, device=None)
Returns a tensor of a predefined shape between -1 and 1 with a normal distribution
source
random_half_normal
random_half_normal ()
Returns a number between 0 and 1 with a half-normal distribution
source
random_normal
random_normal ()
Returns a number between -1 and 1 with a normal distribution
source
get_plot_fig
get_plot_fig (size=None, dpi=100)
source
default_dpi
default_dpi ()
source
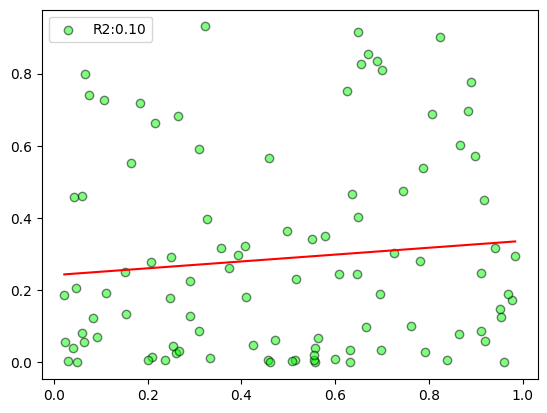
plot_scatter
plot_scatter (x, y, deg=1)
= np.random.rand(100 )= np.random.rand(100 )** 2
source
get_idxs
get_idxs (o, aList)
= random_shuffle(np.arange(100 , 200 ))= np.random.choice(a, 10 , False )= get_idxs(a, b)
source
apply_cmap
apply_cmap (o, cmap)
= np.random.rand(16 , 1 , 40 , 50 )= L(a.shape)1 ] = 3 'viridis' ).shape), s)0 ] = 1 = np.random.rand(1 , 40 , 50 )'viridis' ).shape), s)
source
torch_tile
torch_tile (a, n_tile, dim=0)
2 ), 3 ), tensor([0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 ]))
source
to_tsfresh_df
to_tsfresh_df (ts)
Prepares a time series (Tensor/ np.ndarray) to be used as a tsfresh dataset to allow feature extraction
= torch.rand(16 , 3 , 20 )= to_tsfresh_df(ts)= ts.numpy()= to_tsfresh_df(ts)
source
torch_diff
torch_diff (t, lag=1, pad=True, append=0)
= torch.arange(24 ).reshape(2 ,3 ,4 )1 )[..., 1 :].float ().mean(), 1. )2 )[..., 2 :].float ().mean(), 2. )
source
torch_clamp
torch_clamp (o, min=None, max=None)
Clamp torch.Tensor using 1 or multiple dimensions
source
get_percentile
get_percentile (o, percentile, axis=None)
source
clip_outliers
clip_outliers (o, axis=None)
source
get_outliers_IQR
get_outliers_IQR (o, axis=None, quantile_range=(25.0, 75.0))
= torch.randn(2 ,3 ,100 )type (get_outliers_IQR(t, - 1 )[0 ]), torch.Tensor)= t.numpy()type (get_outliers_IQR(a, - 1 )[0 ]), np.ndarray)25 ).numpy(), get_percentile(a, 25 ))
source
get_robustscale_params
get_robustscale_params (o, sel_vars=None, not_sel_vars=None, by_var=True,
percentiles=(25, 75), eps=1e-06)
Calculates median and inter-quartile range required to robust scaler inputs
= np.random.rand(16 , 3 , 100 )> .8 ] = np.nan= get_robustscale_params(a, by_var= True , percentiles= (25 , 75 ))= (a - median) / IQRsum (),0 )sum (),0 )
source
torch_slice_by_dim
torch_slice_by_dim (t, index, dim=-1, **kwargs)
= torch.rand(5 , 3 )= torch.randint(0 , 3 , (5 , 1 ))# index = [[0, 2], [0, 1], [1, 2], [0, 2], [0, 1]]
tensor([[0.5341],
[0.4543],
[0.0942],
[0.9645],
[0.0405]])
source
torch_nanstd
torch_nanstd (o, dim=None, keepdim=False)
There’s currently no torch.nanstd function
source
torch_nanmean
torch_nanmean (o, dim=None, keepdim=False)
There’s currently no torch.nanmean function
= torch.rand(1000 )100 ] = float ('nan' )assert torch_nanmean(t).item() > 0
source
concat
concat (*ls, dim=0)
Concatenate tensors, arrays, lists, or tuples by a dimension
source
reduce_memory_usage
reduce_memory_usage (df)
source
cls_name
cls_name (o)
'Timer' )
source
rotate_axis2
rotate_axis2 (o, steps=1)
source
rotate_axis1
rotate_axis1 (o, steps=1)
source
rotate_axis0
rotate_axis0 (o, steps=1)
source
random_roll3d
random_roll3d (o, axis=(), replace=False)
Randomly rolls a 3D object along the indicated axes This solution is based on https://stackoverflow.com/questions/20360675/roll-rows-of-a-matrix-independently
source
random_roll2d
random_roll2d (o, axis=(), replace=False)
Rolls a 2D object on the indicated axis This solution is based on https://stackoverflow.com/questions/20360675/roll-rows-of-a-matrix-independently
source
roll3d
roll3d (o, roll1:Union[NoneType,list,int]=None,
roll2:Union[NoneType,list,int]=None,
roll3:Union[NoneType,list,int]=None)
Rolls a 3D object on the indicated axis This solution is based on https://stackoverflow.com/questions/20360675/roll-rows-of-a-matrix-independently
source
roll2d
roll2d (o, roll1:Union[NoneType,list,int]=None,
roll2:Union[NoneType,list,int]=None)
Rolls a 2D object on the indicated axis This solution is based on https://stackoverflow.com/questions/20360675/roll-rows-of-a-matrix-independently
= np.tile(np.arange(10 ), 3 ).reshape(3 , 10 ) * np.array([1 , 10 , 100 ]).reshape(- 1 , 1 )
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[ 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90],
[ 0, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900]])
= [2 , 1 , 0 ])
array([[ 0, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900],
[ 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90],
[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]])
array([[ 7, 8, 9, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
[ 70, 80, 90, 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60],
[700, 800, 900, 0, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600]])
= torch.arange(24 ).reshape(2 ,3 ,4 )1 ], o[0 ])1 ], o[:,0 ])1 ], o[...,0 ])
source
chunks_calculator
chunks_calculator (shape, dtype='float32', n_bytes=1073741824)
*Function to calculate chunks for a given size of n_bytes (default = 1024**3 == 1GB). It guarantees > 50% of the chunk will be filled*
= (1_000 , 10 , 1000 )= 'float32' False )= (54684 , 10 , 1000 )= 'float32' 27342 , - 1 , - 1 ))
source
is_memory_shared
is_memory_shared (a, b)
Check if 2 array-like objects share memory
= np.random.rand(2 ,3 ,4 )= torch.from_numpy(a)True )= np.random.rand(2 ,3 ,4 )= torch.as_tensor(a)True )= np.random.rand(2 ,3 ,4 )= torch.tensor(a)False )
source
assign_in_chunks
assign_in_chunks (a, b, chunksize='auto', inplace=True, verbose=True)
Assigns values in b to an array-like object a using chunks to avoid memory overload. The resulting a retains it’s dtype and share it’s memory. a: array-like object b: may be an integer, float, str, ‘rand’ (for random data), or another array like object. chunksize: is the size of chunks. If ‘auto’ chunks will have around 1GB each.
= np.random.rand(10 ,3 ,4 ).astype('float32' )= a.dtype= id (a)= np.random.rand(10 ,3 ,4 ).astype('float64' )= 2 , inplace= True , verbose= True )id (a), a_id)= np.random.rand(10 ,3 ,4 ).astype('float32' )= a.dtype= id (a)= 1 = 2 , inplace= True , verbose= True )id (a), a_id)= np.random.rand(10 ,3 ,4 ).astype('float32' )= a.dtype= id (a)= 0.5 = 2 , inplace= True , verbose= True )id (a), a_id)= np.random.rand(10 ,3 ,4 ).astype('float32' )= a.dtype= id (a)= 'rand' = 2 , inplace= True , verbose= True )id (a), a_id)
= np.random.rand(10 ,3 ,4 ).astype('float32' )= np.random.rand(10 ,3 ,4 ).astype('float64' )= assign_in_chunks(a, b, chunksize= 2 , inplace= False , verbose= True )True )= np.random.rand(10 ,3 ,4 ).astype('float32' )= 1 = assign_in_chunks(a, b, chunksize= 2 , inplace= False , verbose= True )True )= np.random.rand(10 ,3 ,4 ).astype('float32' )= 0.5 = assign_in_chunks(a, b, chunksize= 2 , inplace= False , verbose= True )True )= np.random.rand(10 ,3 ,4 ).astype('float32' )= 'rand' = assign_in_chunks(a, b, chunksize= 2 , inplace= False , verbose= True )True )
source
create_array
create_array (shape, fname=None, path='./data', on_disk=True,
dtype='float32', mode='r+', fill_value='rand',
chunksize='auto', verbose=True, **kwargs)
mode: ‘r’: Open existing file for reading only. ‘r+’: Open existing file for reading and writing. ‘w+’: Create or overwrite existing file for reading and writing. ‘c’: Copy-on-write: assignments affect data in memory, but changes are not saved to disk. The file on disk is read-only. fill_value: ‘rand’ (for random numbers), int or float chunksize = ‘auto’ to calculate chunks of 1GB, or any integer (for a given number of samples)
= 'X_on_disk' = (100 , 10 , 10 )= create_array(shape, fname, on_disk= True , mode= 'r+' )abs (X).sum (), 0 )del X
= 'X_on_disk' = (100 , 10 , 10 )= create_empty_array(shape, fname, on_disk= True , mode= 'r+' )abs (X).sum (), 0 )= 10 = progress_bar(range (math.ceil(len (X) / chunksize)), leave= False )= 0 for i in pbar:= min (start + chunksize, len (X))= np.random.rand(end - start, X.shape[1 ] , X.shape[2 ])= partial_data= enddel partial_data= X.filenamedel X= np.load(filename, mmap_mode= 'r+' )== 0 ).sum (), 0 )del X
source
np_load_compressed
np_load_compressed (fname=None, path='./data', **kwargs)
source
np_save_compressed
np_save_compressed (arr, fname=None, path='./data', verbose=False,
**kwargs)
= np.random.rand(10 )'X_comp' , path= './data' )= np_load_compressed('X_comp' )
source
np2memmap
np2memmap (arr, fname=None, path='./data', dtype='float32', mode='c',
**kwargs)
Function that turns an ndarray into a memmap ndarray mode: ‘r’: Open existing file for reading only. ‘r+’: Open existing file for reading and writing. ‘w+’: Create or overwrite existing file for reading and writing. ‘c’: Copy-on-write: assignments affect data in memory, but changes are not saved to disk. The file on disk is read-only.
= np.random.rand(10 )= np2memmap(X1, 'X1_test' )type (X1), type (X2))
source
torch_mean_groupby
torch_mean_groupby (o, idxs)
Computes torch mean along axis 0 grouped by the idxs. Need to ensure that idxs have the same order as o
= torch.arange(6 * 2 * 3 ).reshape(6 , 2 , 3 ).float ()= np.array([[0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ], [2 ,3 ]], dtype= object )= torch_mean_groupby(o, idxs)2 ], output[:2 ])2 :4 ].mean(0 ), output[2 ])4 :6 ].mean(0 ), output[3 ])
source
torch_flip
torch_flip (t, dims=-1)
= torch.randn(2 , 3 , 4 )2 ,)), torch_flip(t, dims=- 1 ))
source
torch_masked_to_num
torch_masked_to_num (o, mask, num=0, inplace=False)
source
torch_nan_to_num
torch_nan_to_num (o, num=0, inplace=False)
= torch.rand(2 , 4 , 6 )3 ][x[:, :3 ] < .5 ] = np.nan= torch.isnan(x).sum ()= torch_nan_to_num(x[:, :3 ], inplace= False )sum (), 0 )sum (), nan_values)3 ], inplace= True )sum (), 0 )
= torch.rand(2 , 4 , 6 )= x[:, :3 ] > .5 3 ] = torch_masked_to_num(x[:, :3 ], mask, num= 0 , inplace= False )3 ][mask].sum (), 0 )
= torch.rand(2 , 4 , 6 )= x[:, :3 ] > .5 3 ], mask, num= 0 , inplace= True )3 ][mask].sum (), 0 )
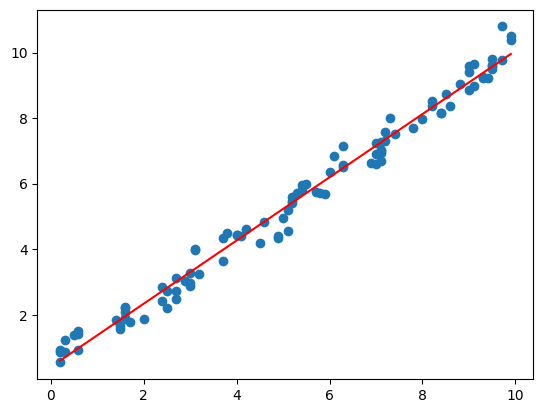
source
mpl_trend
mpl_trend (x, y, deg=1)
= np.sort(np.random.randint(0 , 100 , 100 )/ 10 )= np.random.rand(100 ) + np.linspace(0 , 10 , 100 )= mpl_trend(x, y)'r' )
source
array2digits
array2digits (o, n_digits=None, normalize=True)
source
int2digits
int2digits (o, n_digits=None, normalize=True)
= - 9645 6 ), np.array([ 0 , 0 , - .9 , - .6 , - .4 , - .5 ]))= np.random.randint(- 1000 , 1000 , 10 )5 ).shape, (10 ,5 ))
source
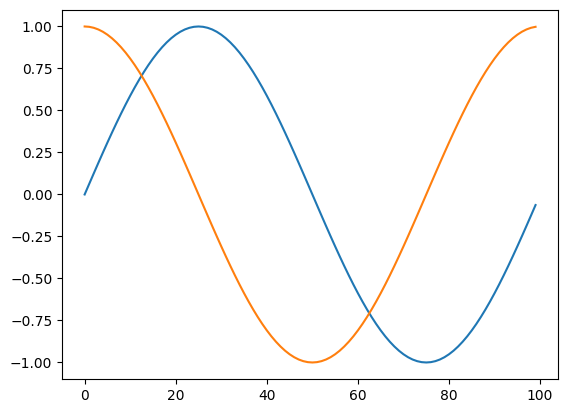
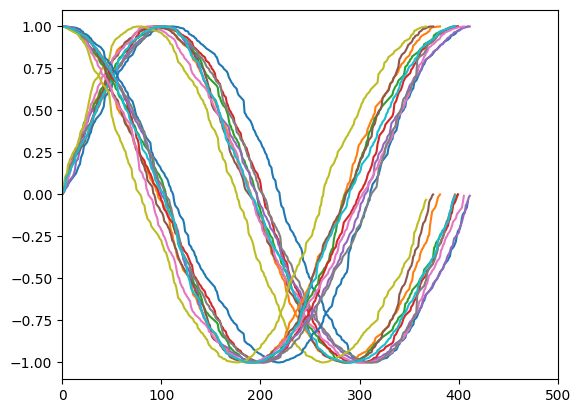
sincos_encoding
sincos_encoding (seq_len, device=None, to_np=False)
= sincos_encoding(100 )
source
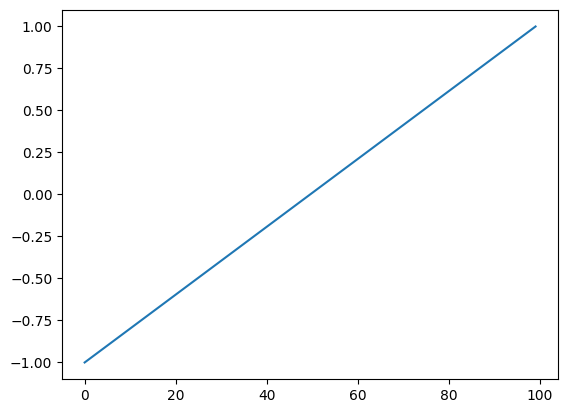
linear_encoding
linear_encoding (seq_len, device=None, to_np=False, lin_range=(-1, 1))
= linear_encoding(100 )
source
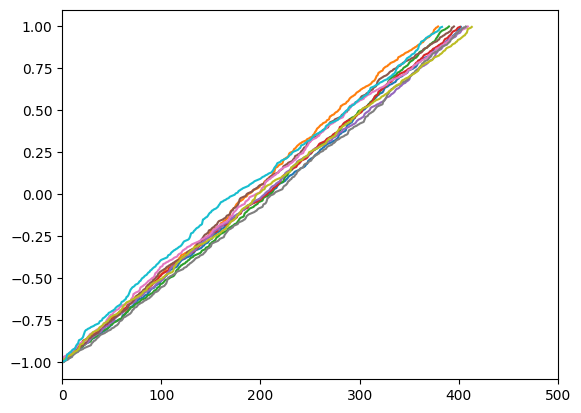
encode_positions
encode_positions (pos_arr, min_val=None, max_val=None, linear=False,
lin_range=(-1, 1))
Encodes an array with positions using a linear or sincos methods
= 10 = 500 = []for i in range (n_samples):= np.arange(- 4000 , 4000 , 10 )= np.random.rand(len (a)) > .5 = a[mask]= np.concatenate([a, np.array([np.nan] * (length - len (a)))])- 1 ,1 ))= np.concatenate(_a, - 1 ).transpose(1 ,0 )= encode_positions(a, linear= False )0 , 500 )
= 10 = 500 = []for i in range (n_samples):= np.arange(- 4000 , 4000 , 10 )= np.random.rand(len (a)) > .5 = a[mask]= np.concatenate([a, np.array([np.nan] * (length - len (a)))])- 1 ,1 ))= np.concatenate(_a, - 1 ).transpose(1 ,0 )= encode_positions(a, linear= True )0 , 500 )
source
sort_generator
sort_generator (generator, bs)
= (i for i in np.random.permutation(np.arange(1000000 )).tolist())= list (sort_generator(generator, 512 ))512 ], sorted (l[:512 ]))
source
get_subset_dict
get_subset_dict (d, keys)
= string.ascii_lowercase= np.arange(len (keys))= {k:v for k,v in zip (keys,values)}'a' , 'k' , 'j' , 'e' ]), {'a' : 0 , 'k' : 10 , 'j' : 9 , 'e' : 4 })
source
remove_dir
remove_dir (directory, verbose=True)
source
create_dir
create_dir (directory, verbose=True)
= "wandb3/wandb2/wandb" assert Path(path).exists()= ["wandb3/wandb2/wandb" , "wandb3/wandb2" , "wandb" ]for p in paths:assert not Path(p).exists()= "wandb3" assert Path(path).exists()assert not Path(path).exists()
wandb3/wandb2/wandb directory created.
wandb3/wandb2/wandb directory removed.
wandb3/wandb2 directory removed.
wandb directory doesn't exist.
wandb3 directory removed.
= 5 def fn(b): return a + b
Writing ./test/mod_dev.py
= "./test/mod_dev.py" while True :if fname[0 ] in "/ ." : fname = fname.split(fname[0 ], 1 )[1 ]else : break if '/' in fname and fname.rsplit('/' , 1 )[0 ] not in sys.path: sys.path.append(fname.rsplit('/' , 1 )[0 ])= import_file_as_module(fname)3 ), 8 )= sys.path[:- 1 ]'./test/' )
source
named_partial
named_partial (name, func, *args, **kwargs)
Create a partial function with a name
def add_1(x, add= 1 ): return x+ add1 ), 2 )= partial(add_1, add= 2 )2 ), 4 )str (add_2), "add_2" )= named_partial('add_2' , add_1, add= 2 )2 ), 4 )str (add_2), "add_2" )class _A():def __init__ (self , add= 1 ): self .add = adddef __call__ (self , x): return x + self .add1 ), 2 )= partial(_A, add= 2 )1 ), 3 )str (_A2), '_A2' )= named_partial('_A2' , _A, add= 2 )1 ), 3 )str (_A2), '_A2' )
source
dict2attrdict
dict2attrdict (d:dict)
Converts a (nested) dict to an AttrDict.
source
attrdict2dict
attrdict2dict (d:dict)
Converts a (nested) AttrDict dict to a dict.
# Test attrdict2dict = AttrDict({'a' : 1 , 'b' : AttrDict({'c' : 2 , 'd' : 3 })})'a' : 1 , 'b' : {'c' : 2 , 'd' : 3 }})# Test dict2attrdict = {'a' : 1 , 'b' : {'c' : 2 , 'd' : 3 }}'a' : 1 , 'b' : AttrDict({'c' : 2 , 'd' : 3 })}))
source
get_config
get_config (file_path)
Gets a config from a yaml file.
source
yaml2dict
yaml2dict (file_path, attrdict=True)
Converts a yaml file to a dict (optionally AttrDict).
file_path
a path to a yaml file
attrdict
bool
True
if True, convert output to AttrDict
source
dict2yaml
dict2yaml (d, file_path, sort_keys=False)
Converts a dict to a yaml file.
d
a dict
file_path
a path to a yaml file
sort_keys
bool
False
if True, sort the keys
/ train_script.py # (required) Path to training script. # (required) Specify the search strategy: grid, random or bayes # (required) Specify parameters bounds to search. 32 , 64 , 128 ]3 , 6 , 9 , 12 ]min : 0. max : 0.5 0.001 , 0.003 , 0.01 , 0.03 , 0.1 ]10 , 15 , 20 ]32 , 64 , 128 ]# This must match one of the metrics in the training script type : hyperband3
Writing sweep_config.yaml
= "sweep_config.yaml" = yaml2dict(fname)print (sweep_config)'bayes' )'metric' ], {'name' : 'accuracy' , 'goal' : 'maximize' })
{'program': 'wandb_scripts/train_script.py', 'method': 'bayes', 'parameters': {'bs': {'values': [32, 64, 128]}, 'depth': {'values': [3, 6, 9, 12]}, 'fc_dropout': {'distribution': 'uniform', 'min': 0.0, 'max': 0.5}, 'lr_max': {'values': [0.001, 0.003, 0.01, 0.03, 0.1]}, 'n_epoch': {'values': [10, 15, 20]}, 'nb_filters': {'values': [32, 64, 128]}}, 'name': 'LSST_sweep_01', 'metric': {'name': 'accuracy', 'goal': 'maximize'}, 'early_terminate': {'type': 'hyperband', 'min_iter': 3}, 'project': 'LSST_wandb_hpo'}
source
get_cat_cols
get_cat_cols (df)
source
get_cont_cols
get_cont_cols (df)
source
str2index
str2index (o)
source
map_array
map_array (arr, dim=1)
source
get_mapping
get_mapping (arr, dim=1, return_counts=False)
= np.asarray(alphabet[np.random.randint(0 ,15 ,30 )]).reshape(10 ,3 )= np.asarray(ALPHABET[np.random.randint(6 ,10 ,30 )]).reshape(10 ,3 )= concat(a,b,dim= 1 )= get_mapping(x, dim= 1 , return_counts= True )
(array([['d', 'k', 'l', 'I', 'I', 'G'],
['g', 'i', 'l', 'I', 'J', 'I'],
['e', 'l', 'n', 'G', 'H', 'I'],
['e', 'l', 'a', 'I', 'H', 'G'],
['k', 'l', 'b', 'I', 'I', 'J'],
['c', 'f', 'k', 'I', 'H', 'I'],
['e', 'j', 'f', 'I', 'H', 'J'],
['n', 'd', 'g', 'G', 'J', 'J'],
['d', 'f', 'a', 'I', 'H', 'H'],
['i', 'c', 'm', 'J', 'G', 'G']], dtype='<U1'),
[(#7) ['c','d','e','g','i','k','n'],
(#7) ['c','d','f','i','j','k','l'],
(#8) ['a','b','f','g','k','l','m','n'],
(#3) ['G','I','J'],
(#4) ['G','H','I','J'],
(#4) ['G','H','I','J']],
[7, 7, 8, 3, 4, 4])
= np.asarray(alphabet[np.random.randint(0 ,15 ,30 )]).reshape(10 ,3 )1 )
(array([['i', 'm', 'd'],
['h', 'm', 'g'],
['i', 'g', 'd'],
['k', 'm', 'n'],
['n', 'j', 'l'],
['n', 'l', 'i'],
['f', 'c', 'k'],
['i', 'm', 'a'],
['l', 'i', 'f'],
['k', 'o', 'g']], dtype='<U1'),
array([[2, 5, 1],
[1, 5, 3],
[2, 1, 1],
[3, 5, 7],
[5, 3, 6],
[5, 4, 4],
[0, 0, 5],
[2, 5, 0],
[4, 2, 2],
[3, 6, 3]]),
array([[2, 5, 1],
[1, 5, 3],
[2, 1, 1],
[3, 5, 7],
[5, 3, 6],
[5, 4, 4],
[0, 0, 5],
[2, 5, 0],
[4, 2, 2],
[3, 6, 3]]))
source
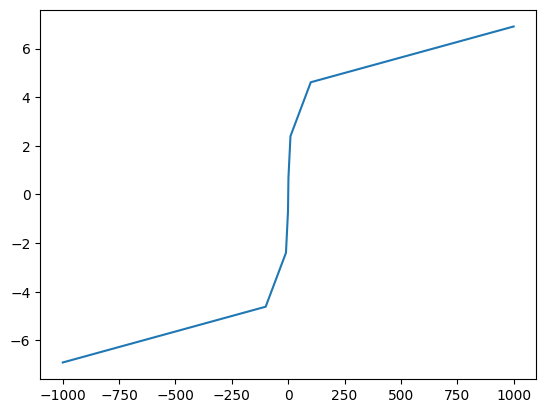
log_tfm
log_tfm (o, inplace=False)
Log transforms an array-like object with positive and/or negative values
= np.asarray([- 1000 , - 100 , - 10 , - 1 , 0 , 1 , 10 , 100 , 1000 ]).astype(float )False ))
= tensor([- 1000 , - 100 , - 10 , - 1 , 0 , 1 , 10 , 100 , 1000 ]).float ()False ))
source
to_sincos_time
to_sincos_time (arr, max_value)
= np.sort(np.random.rand(100 ) * 5 )= to_sincos_time(arr, 5 )
source
plot_feature_dist
plot_feature_dist (X, percentiles=[0, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, 75, 90,
95, 99, 99.5, 99.9, 100])
= np.random.rand(10 , 3 , 100 )= [0 ,0.1 ,0.5 ,1 ,5 ,10 ,25 ,50 ,75 ,90 ,95 ,99 ,99.5 ,99.9 ,100 ])
source
rolling_moving_average
rolling_moving_average (o, window=2)
= np.arange(60 ).reshape(2 ,3 ,10 ).astype(float )= torch.arange(60 ).reshape(2 ,3 ,10 ).float ()= 3 ), rolling_moving_average(t, window= 3 ).numpy())print (t)print (rolling_moving_average(t, window= 3 ))
tensor([[[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9.],
[10., 11., 12., 13., 14., 15., 16., 17., 18., 19.],
[20., 21., 22., 23., 24., 25., 26., 27., 28., 29.]],
[[30., 31., 32., 33., 34., 35., 36., 37., 38., 39.],
[40., 41., 42., 43., 44., 45., 46., 47., 48., 49.],
[50., 51., 52., 53., 54., 55., 56., 57., 58., 59.]]])
tensor([[[ 0.0000, 0.5000, 1.0000, 2.0000, 3.0000, 4.0000, 5.0000,
6.0000, 7.0000, 8.0000],
[10.0000, 10.5000, 11.0000, 12.0000, 13.0000, 14.0000, 15.0000,
16.0000, 17.0000, 18.0000],
[20.0000, 20.5000, 21.0000, 22.0000, 23.0000, 24.0000, 25.0000,
26.0000, 27.0000, 28.0000]],
[[30.0000, 30.5000, 31.0000, 32.0000, 33.0000, 34.0000, 35.0000,
36.0000, 37.0000, 38.0000],
[40.0000, 40.5000, 41.0000, 42.0000, 43.0000, 44.0000, 45.0000,
46.0000, 47.0000, 48.0000],
[50.0000, 50.5000, 51.0000, 52.0000, 53.0000, 54.0000, 55.0000,
56.0000, 57.0000, 58.0000]]])
source
fbfill_sequence
fbfill_sequence (o)
Forward and backward fills an array-like object alongside sequence dimension
source
bfill_sequence
bfill_sequence (o)
Backward fills an array-like object alongside sequence dimension
source
ffill_sequence
ffill_sequence (o)
Forward fills an array-like object alongside sequence dimension
= np.arange(80 ).reshape(2 , 4 , 10 ).astype(float )= np.random.rand(* a.shape)> .8 ] = np.nan= torch.from_numpy(a)
tensor([[[ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., nan],
[10., 11., nan, nan, 14., 15., nan, 17., nan, 19.],
[20., 21., 22., 23., nan, 25., 26., 27., 28., 29.],
[30., 31., 32., 33., nan, 35., 36., 37., 38., 39.]],
[[40., 41., 42., 43., 44., 45., 46., 47., nan, 49.],
[nan, 51., nan, 53., 54., 55., nan, 57., 58., 59.],
[60., 61., 62., 63., 64., nan, nan, 67., 68., 69.],
[70., nan, 72., 73., 74., 75., 76., nan, 78., 79.]]],
dtype=torch.float64)
# forward fill = ffill_sequence(a)print (filled_a)= np.isnan(filled_a)~ m], ffill_sequence(t).numpy()[~ m])
[[[ 0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 8.]
[10. 11. 11. 11. 14. 15. 15. 17. 17. 19.]
[20. 21. 22. 23. 23. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29.]
[30. 31. 32. 33. 33. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39.]]
[[40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 47. 49.]
[nan 51. 51. 53. 54. 55. 55. 57. 58. 59.]
[60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 64. 64. 67. 68. 69.]
[70. 70. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 76. 78. 79.]]]
# backward fill = bfill_sequence(a)print (filled_a)= np.isnan(filled_a)~ m], bfill_sequence(t).numpy()[~ m])
[[[ 0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. nan]
[10. 11. 14. 14. 14. 15. 17. 17. 19. 19.]
[20. 21. 22. 23. 25. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29.]
[30. 31. 32. 33. 35. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39.]]
[[40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 49. 49.]
[51. 51. 53. 53. 54. 55. 57. 57. 58. 59.]
[60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 67. 67. 67. 68. 69.]
[70. 72. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 78. 78. 79.]]]
# forward & backward fill = fbfill_sequence(a)print (filled_a)= np.isnan(filled_a)~ m], fbfill_sequence(t).numpy()[~ m])
[[[ 0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 8.]
[10. 11. 11. 11. 14. 15. 15. 17. 17. 19.]
[20. 21. 22. 23. 23. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29.]
[30. 31. 32. 33. 33. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39.]]
[[40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 47. 49.]
[51. 51. 51. 53. 54. 55. 55. 57. 58. 59.]
[60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 64. 64. 67. 68. 69.]
[70. 70. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 76. 78. 79.]]]
source
dummify
dummify (o:Union[numpy.ndarray,torch.Tensor], by_var:bool=True,
inplace:bool=False, skip:Optional[list]=None, random_state=None)
Shuffles an array-like object along all dimensions or dimension 1 (variables) if by_var is True.
= np.random.rand(2 ,3 ,10 )= arr.copy()= dummify(arr)= True )
= torch.rand(2 ,3 ,10 )= t.clone()= dummify(t)= True )
source
shuffle_along_axis
shuffle_along_axis (o, axis=-1, random_state=None)
= np.arange(60 ).reshape(2 ,3 ,10 ) + 10 = shuffle_along_axis(X,(0 , - 1 ), random_state= 23 )13 , 15 , 41 , 14 , 40 , 49 , 18 , 42 , 47 , 46 ],28 , 56 , 53 , 50 , 52 , 25 , 24 , 57 , 51 , 59 ],34 , 30 , 38 , 35 , 69 , 66 , 63 , 67 , 61 , 62 ]],19 , 10 , 11 , 16 , 43 , 12 , 17 , 48 , 45 , 44 ],23 , 20 , 26 , 22 , 21 , 27 , 58 , 29 , 54 , 55 ],36 , 31 , 39 , 60 , 33 , 68 , 37 , 32 , 65 , 64 ]]]))
source
analyze_array
analyze_array (o, bins=100, density=False, feature_names=None,
clip_outliers_plot=False, quantile_range=(25.0, 75.0),
percentiles=[1, 25, 50, 75, 99], text_len=12, figsize=(10,
6))
source
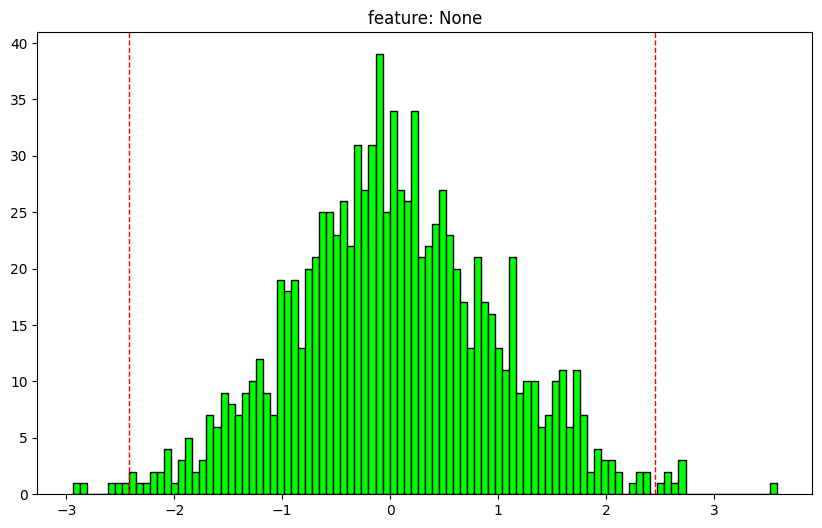
analyze_feature
analyze_feature (feature, bins=100, density=False, feature_name=None,
clip_outliers_plot=False, quantile_range=(25.0, 75.0),
percentiles=[1, 25, 50, 75, 99], text_len=12,
figsize=(10, 6))
= np.random.normal(size= (1000 ))
array shape: (1000,)
dtype: float64
nan values: 0.0%
max: 3.581094060980321
1: -2.1615590829115185
25: -0.5910961139851849
50: -0.002247946765973052
75: 0.6259274030927355
99: 2.3412961380708084
min: -2.9413736207935037
outlier min: -2.416631389602066
outlier max: 2.4514626787096163
outliers: 1.3%
mean: 0.0252125277963861
std: 0.946955486669799
normal dist: True
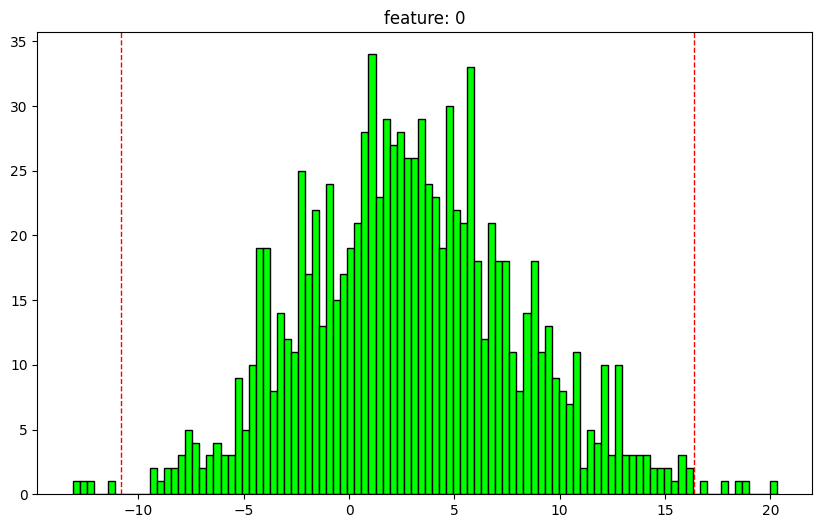
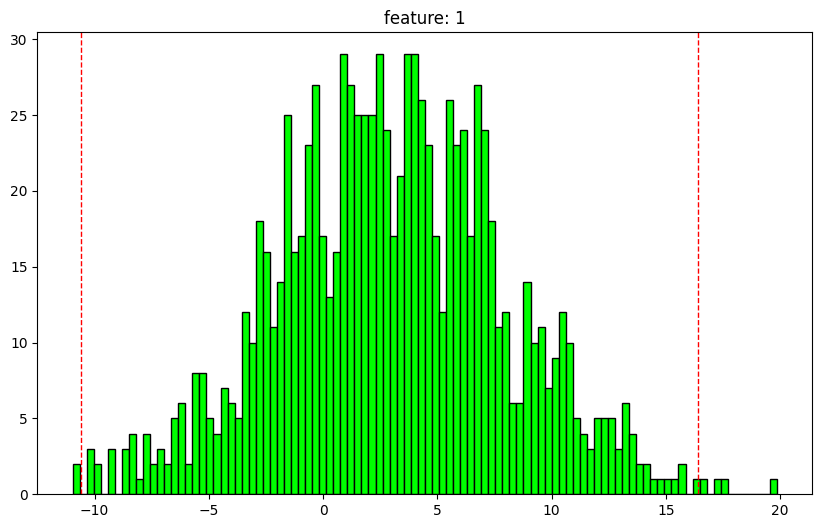
= np.random.normal(size= (1000 ,2 ))= np.random.normal(3 , 5 , size= (1000 ,2 ))= x1 + x2
array shape: (1000, 2)
0 feature: 0
dtype: float64
nan values: 0.0%
max: 20.323075761234193
1: -8.260661592413742
25: -0.6268118569038604
50: 2.7491159998190335
75: 6.1659732833324234
99: 15.387037197243288
min: -13.122296090020368
outlier min: -10.815989567258287
outlier max: 16.35515099368685
outliers: 0.9%
mean: 2.9347218553275445
std: 5.134940196769919
normal dist: True
1 feature: 1
dtype: float64
nan values: 0.0%
max: 19.86661808715871
1: -8.727124941895372
25: -0.45908489661153007
50: 2.875134866985423
75: 6.288434737224429
99: 14.424046274543118
min: -10.963913297285615
outlier min: -10.58036434736547
outlier max: 16.409714187978366
outliers: 0.6%
mean: 2.9552584127690014
std: 4.99683092772426
normal dist: True
source
get_relpath
get_relpath (path)
source
to_root_path
to_root_path (path)
Converts a path to an absolute path from the root directory of the repository.
source
get_root
get_root ()
Returns the root directory of the git repository.
source
split_in_chunks
split_in_chunks (o, chunksize, start=0, shuffle=False, drop_last=False)
= np.arange(5 , 15 )3 , drop_last= False ), [array([5 , 6 , 7 ]), array([ 8 , 9 , 10 ]), array([11 , 12 , 13 ]), array([14 ])])3 , drop_last= True ), [array([5 , 6 , 7 ]), array([ 8 , 9 , 10 ]), array([11 , 12 , 13 ])])3 , start= 2 , drop_last= True ), [array([7 , 8 , 9 ]), array([10 , 11 , 12 ])])
source
load_object
load_object (file_path)
source
save_object
save_object (o, file_path, verbose=True)
= np.arange(100 )= 'data/test' )= load_object('data/test.pkl' )
data directory already exists.
ndarray saved as data/test.pkl
= L([[[0 ,1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ], [5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ]],[[10 ,11 ,12 ,13 ,14 ], [15 ,16 ,17 ,18 ,19 ]]])= Path('data/test' ))= load_object('data/test' )
data directory already exists.
L saved as data/test.pkl
source
get_idxs_to_keep
get_idxs_to_keep (o, cond, crit='all', invert=False, axis=(1, 2),
keepdims=False)
= np.random.rand(100 , 2 , 10 )> .95 ] = np.nan= get_idxs_to_keep(a, np.isfinite)if idxs_to_keep.size> 0 :sum (), 0 )
source
zerofy
zerofy (a, stride, keep=False)
Create copies of an array setting individual/ group values to zero
= 3 = np.arange(2 * 5 ).reshape(2 ,5 ) + 1 = False )
array([[[ 0., 0., 3., 4., 5.],
[ 6., 7., 8., 9., 10.]],
[[ 1., 2., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 6., 7., 8., 9., 10.]],
[[ 1., 2., 3., 4., 5.],
[ 0., 0., 8., 9., 10.]],
[[ 1., 2., 3., 4., 5.],
[ 6., 7., 0., 0., 0.]]])
source
feat2list
feat2list (o)
= 'a' 'a' ])= ['a' , 'b' ]'a' , 'b' ])= None
source
smallest_dtype
smallest_dtype (num, use_unsigned=False)
Find the smallest dtype that can safely hold num
3654 ), 'int16' )2048. ), 'float16' )365454 ), 'int32' )365454. ), 'float32' )3654545134897 ), 'int64' )
source
plot_forecast
plot_forecast (X_true, y_true, y_pred, sel_vars=None, idx=None,
figsize=(8, 4), n_samples=1)
source
str2callable
str2callable (object_path:str=None)
Transform a string into a callable object without importing it in the script.
object_path
str
None
The string representing the object path.
# test showing you don't need to import the object in the script. The library needs to be installed though. try :except Exception as e:print (0 , e)try :except Exception as e:print (1 , e)try := eval ("pyts.image.GramianAngularField(method='summation')" )print (f"2 success: { gasf} " )except Exception as e:print (2 , e)try := str2callable("pyts.image.GramianAngularField(method='summation')" )print (f"3 success: { gasf} " )except Exception as e:print (3 , e)
0 name 'pyts' is not defined
1 name 'pyts' is not defined
2 name 'pyts' is not defined
3 success: GramianAngularField()